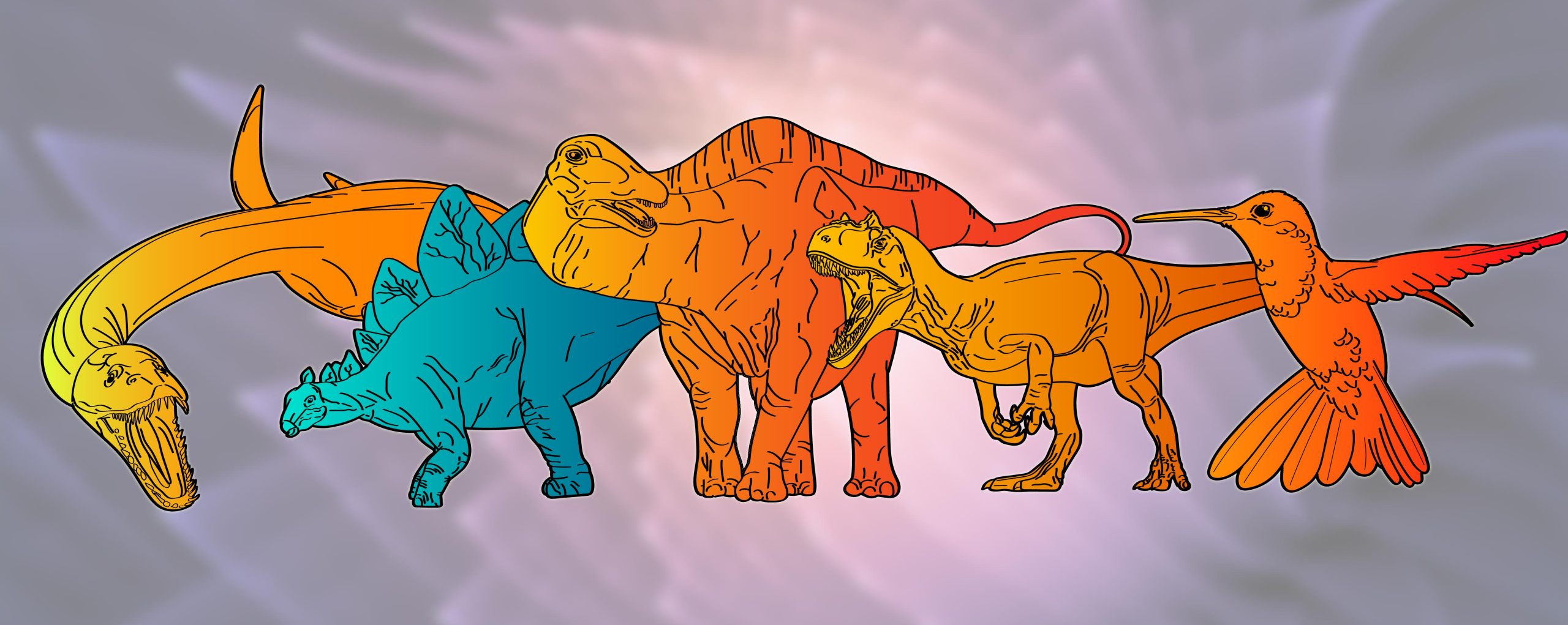
Schematic drawing of a subset of the animals that had been investigated as a part of the evaluation. Metabolic charges and ensuing thermophysiological strategies are coloration-coded, orange hues symbolize high metabolic charges coinciding with warm-bloodedness, and blue hues symbolize low-metabolic charges coinciding with frigid-bloodedness. From left to factual: Plesiosaurus, Stegosaurus, Diplodocus, Allosaurus, Calypte (standard hummingbird). Credit score: © J. Wiemann
Paleontologists were debating for decades whether dinosaurs had been warm-blooded, love standard mammals and birds, or frigid-blooded, love standard reptiles. Intellectual whether dinosaurs had been warm- or frigid-blooded would possibly perhaps well give us clues about how active they had been and what their day to day lives had been love, but previous strategies to resolve their warm- or frigid-bloodedness — how fast their metabolisms would possibly perhaps well turn oxygen into vitality — had been inconclusive. Nonetheless, in a brand novel paper revealed within the journal Nature, scientists are unveiling a novel system for finding out dinosaurs’ metabolic charges, the usage of clues in their bones that indicated how distinguished the person animals breathed in their closing hour of existence.
“Here’s essentially attractive for us as paleontologists — the demand of whether dinosaurs had been warm- or frigid-blooded is one in all the oldest questions in paleontology, and now we whisper we now score a consensus, that virtually all dinosaurs had been warm-blooded,” says Jasmina Wiemann, the paper’s lead creator and a postdoctoral researcher at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech).
“The novel proxy developed by Jasmina Wiemann permits us to straight infer metabolism in extinct organisms, one thing that we had been most productive dreaming about factual just a few years ago. We also learned diversified metabolic charges characterizing diversified teams, which modified into as soon as previously fast essentially based on diversified strategies, but never straight tested,” says Matteo Fabbri, a postdoctoral researcher at the Enviornment Museum in Chicago and one in all the gaze’s authors.
Folks veritably focus on metabolism by approach of how easy it’s some distance for any individual to stay in form, but at its core, “metabolism is how successfully we convert the oxygen that we breathe into chemical vitality that fuels our body,” says Wiemann, who is affiliated with Yale College and the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County.
Diminutive glimpse of extracted soft tissues from the bones of one in all the dinosaur specimens (Allosaurus) that had been investigated for metabolic signals (metabolic crosslinks) within the fossilization products of the proteinaceous bone matrix. Fossilization introduces additional crosslinks that, along with metabolic crosslinks, generate the characteristic brown coloration of the fossil extracellular matrix which holds bone cells (sad, ramifying constructions) and blood vessels (tube-love progress within the heart) in build. Credit score: © J. Wiemann
Animals with a high metabolic charge are endothermic, or warm-blooded; warm-blooded animals love birds and mammals pick in a entire bunch oxygen and want to burn hundreds of energy in uncover to protect their body temperature and stay active. Icy-blooded, or ectothermic, animals love reptiles breathe less and enjoy less. Their standard of living is less energetically costly than a sizzling-blooded animal’s, but it definitely comes at a designate: frigid-blooded animals are reliant on the open air world to abet their bodies at the factual temperature to function (love a lizard basking within the solar), and so they’re inclined to be less active than warm-blooded creatures.
With birds being warm-blooded and reptiles being frigid-blooded, dinosaurs had been caught right via a debate. Birds are the top seemingly dinosaurs that survived the mass extinction at the conclude of the Cretaceous, but dinosaurs (and by extension, birds) are technically reptiles — open air of birds, their closest residing relatives are crocodiles and alligators. So would that accomplish dinosaurs warm-blooded, or frigid-blooded?
“Here’s essentially attractive for us as paleontologists — the demand of whether dinosaurs had been warm- or frigid-blooded is one in all the oldest questions in paleontology, and now we whisper we now score a consensus, that virtually all dinosaurs had been warm-blooded.” — Jasmina Wiemann
Scientists score tried to glean dinosaurs’ metabolic charges from chemical and osteohistological analyses of their bones. “In the past, folks score checked out dinosaur bones with isotope geochemistry that in point of fact works love a paleo-thermometer,” says Wiemann — researchers search for the minerals in a fossil and resolve what temperatures these minerals would score in. “It’s a terribly frosty approach and it modified into as soon as essentially innovative when it got right here out, and it continues to present very attractive insights into the physiology of extinct animals. But we’ve realized that we don’t essentially realize yet how fossilization processes swap the isotope signals that we win, so it’s some distance onerous to unambiguously compare the guidelines from fossils to straightforward animals.”
One more system for finding out metabolism is the progress charge. “Whereas you gaze at a pass-a part of dinosaur bone tissue, you would perhaps perhaps well most doubtless also glimpse a chain of lines, love tree rings, that correspond to years of progress,” says Fabbri. “It is seemingly you’ll perhaps perhaps depend the lines of progress and the distance between them to undercover agent how snappy the dinosaur grew. The restrict depends on the approach you transform progress charge estimates into metabolism: rising faster or slower can score more to accomplish with the animal’s stage in existence than with its metabolism, love how we develop faster when we’re young and slower when we’re older.”
The novel system proposed by Wiemann, Fabbri, and their colleagues doesn’t gaze at the minerals novel in bone or how fast the dinosaur grew. As an different, they gaze at one in all the most typical hallmarks of metabolism: oxygen exercise. When animals breathe, aspect products score that react with proteins, sugars, and lipids, leaving within the abet of molecular “raze.” This raze is amazingly actual and water-insoluble, so it’s preserved all around the fossilization job. It leaves within the abet of a file of how distinguished oxygen a dinosaur modified into as soon as inhaling, and thus, its metabolic charge.
“We live within the sixth mass extinction, so it’s some distance serious for us to score how standard and extinct animals physiologically replied to previous native climate swap and environmental perturbations, so that the past can uncover biodiversity conservation within the novel and uncover our future actions.” — Jasmina Wiemann
The researchers hunted for these bits of molecular raze in sad-colored fossil femurs, due to these sad colours indicate that a entire bunch natural topic are preserved. They examined the fossils the usage of Raman and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy — “these strategies work love laser microscopes, we can mainly quantify the abundance of these molecular markers that advise us about the metabolic charge,” says Wiemann. “It is miles a in particular ravishing diagram to paleontologists, due to it’s some distance non-negative.”
The team analyzed the femurs of 55 diversified teams of animals, in conjunction with dinosaurs, their flying cousins the pterosaurs, their more some distance away marine relatives the plesiosaurs, and stylish birds, mammals, and lizards. They in comparison the amount of breathing-linked molecular byproducts with the acknowledged metabolic charges of the residing animals and primitive these files to infer the metabolic charges of the extinct ones.
The team learned that dinosaurs’ metabolic charges had been most often high. There are two mountainous teams of dinosaurs, the saurischians and the ornithischians — lizard hips and chicken hips. The chicken-hipped dinosaurs, love Triceratops and Stegosaurus, had low metabolic charges identical to these of frigid-blooded standard animals. The lizard-hipped dinosaurs, in conjunction with theropods and the sauropods — the two-legged, more chicken-love predatory dinosaurs love Velociraptor and T. rex and the enormous, prolonged-necked herbivores love Brachiosaurus — had been warm- and even sizzling-blooded. The researchers had been a great deal surprised to rep that hundreds of these dinosaurs weren’t factual warm-blooded — they had metabolic charges identical to straightforward birds, distinguished increased than mammals. These outcomes complement previous self sustaining observations that hinted at such trends but would possibly perhaps well no longer present command proof, thanks to the dearth of a command proxy to infer metabolism.
These findings, the researchers speak, can present us fundamentally novel insights into what dinosaurs’ lives had been love.
“Dinosaurs with lower metabolic charges would were, to a point, reckoning on exterior temperatures,” says Wiemann. “Lizards and turtles sit within the solar and bask, and we would possibly perhaps deserve to make a choice into legend identical ‘behavioral’ thermoregulation in ornithischians with exceptionally low metabolic charges. Icy-blooded dinosaurs also will score had to migrate to warmer climates all around the frigid season, and native climate would possibly perhaps were a selective ingredient for the place hundreds of these dinosaurs would possibly perhaps well are residing.”
On the diversified hand, she says, the sizzling-blooded dinosaurs would were more active and would score wished to enjoy plenty. “The contemporary-blooded huge sauropods had been herbivores, and it would possibly perhaps well pick hundreds of plant topic to feed this metabolic system. They’d very efficient digestive systems, and since they had been so mountainous, it most doubtless modified into as soon as more of an field for them to chill down than to warmth up.” In the period in-between, the theropod dinosaurs — the neighborhood that comprises birds — developed high metabolisms even sooner than some of their participants evolved flight.
“Reconstructing the biology and physiology of extinct animals is one in all the hardest issues to accomplish in paleontology. This novel gaze provides a conventional fragment of the puzzle in working out the evolution of physiology in deep time and enhances previous proxies primitive to investigate these questions. We are able to now infer body temperature via isotopes, progress strategies via osteohistology, and metabolic charges via chemical proxies,” says Fabbri.
As properly as to giving us insights into what dinosaurs had been love, this gaze also helps us better realize the enviornment around us at the present time. Dinosaurs, with the exception of birds, died out in a mass extinction 65 million years ago when an asteroid struck the Earth. “Having a high metabolic charge has most often been fast as one in all the major advantages by approach of surviving mass extinctions and successfully radiating in a while,” says Wiemann — some scientists score proposed that birds survived while the non-avian dinosaurs died thanks to the birds’ increased metabolic capacity. But this gaze, Wiemann says, helps to level that this isn’t factual: many dinosaurs with chicken-love, unprecedented metabolic capacities went extinct.
“We live within the sixth mass extinction,” says Wiemann, “so it’s some distance serious for us to score how standard and extinct animals physiologically replied to previous native climate swap and environmental perturbations, so that the past can uncover biodiversity conservation within the novel and uncover our future actions.”
Reference: “Fossil biomolecules indicate an avian metabolism within the ancestral dinosaur” by Jasmina Wiemann, Iris Menéndez, Jason M. Crawford, Matteo Fabbri, Jacques A. Gauthier, Pincelli M. Hull, Mark A. Norell and Derek E. G. Briggs, 25 Would possibly perhaps perhaps 2022, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04770-6