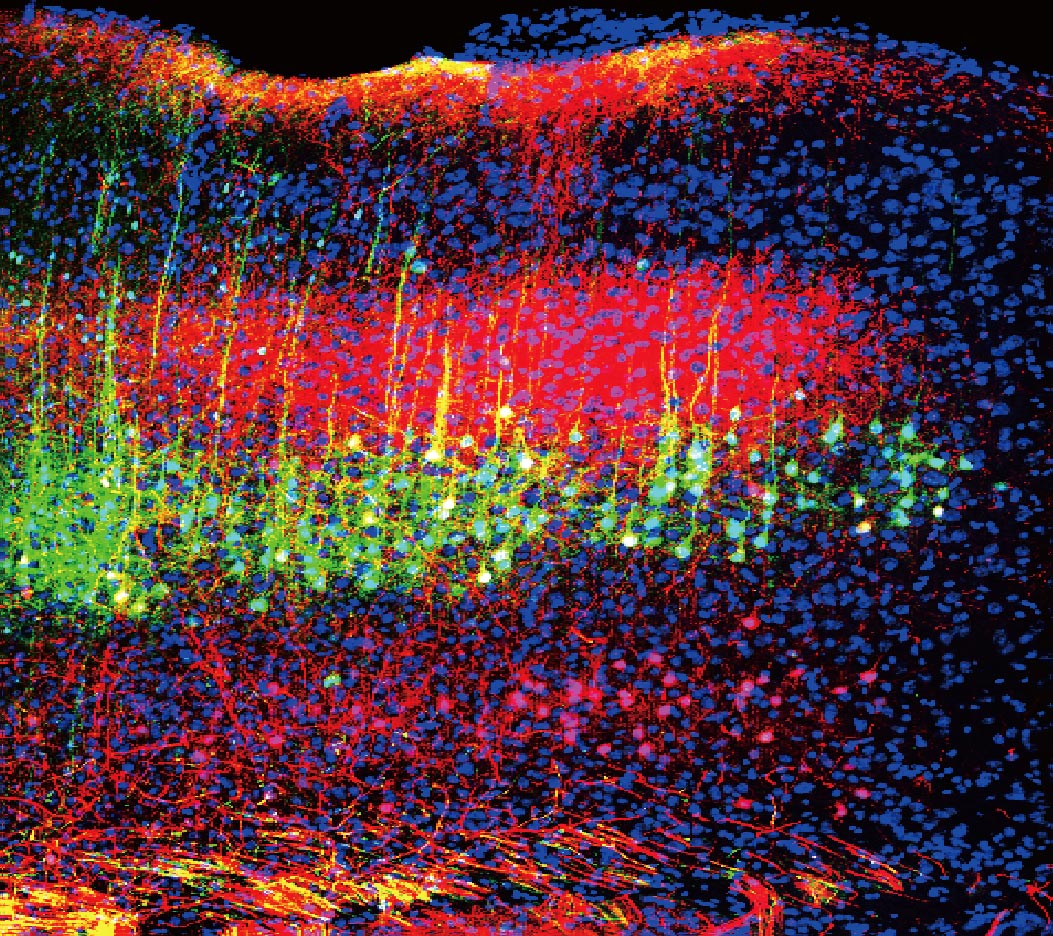
Sound reduces disaster in mice by reducing the assignment of neurons within the brain’s auditory cortex (inexperienced and magenta) that project to the thalamus. Credit: Wenjie Zhou
Scientists Quiz How Sound Reduces Anguish in MiceThe neural mechanisms by which sound blunts disaster in mice contain been identified by an international team of researchers. Published on July 7, 2022, within the journal Science, the findings would perhaps perchance describe the improvement of safer suggestions to treat disaster. The search used to be led by scientists on the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Analysis (NIDCR); the University of Science and Abilities of China, Hefei; and Anhui Medical University, Hefei, China. NIDCR is phase of the National Institutes of Health.
“We want more purposeful suggestions of managing acute and chronic disaster, and that begins with gaining an even bigger working out of the important neural processes that secure watch over disaster,” acknowledged NIDCR Director Rena D’Souza, D.D.S., Ph.D. “By uncovering the circuitry that mediates the disaster-reducing effects of sound in mice, this search adds serious files that would perhaps perchance within the extinguish describe contemporary approaches for disaster therapy.”
“We were if truth be told shocked that the intensity of sound, and no longer the category or perceived pleasantness of sound would matter.” — Yuanyuan (Kevin) Liu, Ph.D.
Human experiences dating assist to 1960 contain demonstrated that tune and other styles of sound can encourage support acute and chronic disaster, alongside with disaster after dental and scientific surgical treatment, labor and provide, and most cancers. However, it used to be unclear how the brain generates this disaster low cost, or analgesia.
“Human brain imaging experiences contain implicated definite areas of the brain in tune-triggered analgesia, but these are most sharp associations,” acknowledged co-senior author Yuanyuan (Kevin) Liu, Ph.D., a Stadtman tenure-song investigator at NIDCR. “In animals, we are in a position to more fully detect and manipulate the circuitry to establish the neural substrates eager.”
The scientists first exposed mice with inflamed paws to three styles of sound: a pleasing allotment of classical tune, an unsuitable rearrangement of the same allotment, and white noise. Surprisingly, all three styles of sound, when performed at a low intensity relative to background noise (about the stage of a remark) diminished disaster sensitivity within the mice. Bigger intensities of the same sounds had no kind on animals’ disaster responses.
“We were if truth be told shocked that the intensity of sound, and no longer the category or perceived pleasantness of sound would matter,” Liu acknowledged.
To search out the brain circuitry underlying this vogue, the researchers dilapidated non-infectious viruses coupled with fluorescent proteins to hint connections between brain areas. They identified a route from the auditory cortex, which receives and processes files about sound, to the thalamus, which acts as a relay blueprint for sensory signals, alongside with disaster, from the physique. In freely transferring mice, low-intensity white noise diminished the assignment of neurons on the receiving pause of the pathway within the thalamus.
Within the absence of sound, suppressing the pathway with light- and little molecule-based ways mimicked the disaster-blunting effects of low-intensity noise, whereas turning on the pathway restored animals’ sensitivity to disaster.
Liu acknowledged it is unclear if same brain processes are concerned about folks, or whether or no longer other aspects of sound, resembling its perceived cohesion or pleasantness, are crucial for human disaster relief.
“We don’t know if human tune capacity something else to rodents, but it surely has many different meanings to folks—you’ve got tons of emotional substances,” he acknowledged.
The results would perhaps perchance give scientists a starting level for experiences to resolve whether or no longer the animal findings apply to folks, and within the extinguish would perhaps perchance describe the improvement of safer alternate choices to opioids for treating disaster.
Reference: “Sound induces analgesia thru corticothalamic circuits” by Wenjie Zhou, Chonghuan Ye, Haitao Wang, Yu Mao, Weijia Zhang, An Liu, Chen-Ling Yang, Tianming Li, Lauren Hayashi, Wan Zhao, Lin Chen, Yuanyuan Liu, Wenjuan Tao and Zhi Zhang, 7 July 2022, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.abn4663
This research used to be supported by the NIDCR Division of Intramural Analysis. Give a get rid of to additionally came from the National Key Analysis and Trend Program of China Brain Science and Brain-Treasure Intelligence Abilities, National Natural Science Basis of China, Science Fund for Inventive Analysis Groups of the National Natural Science Basis of China, CAS Mission for Young Scientists in Fundamental Analysis, Natural Science Basis of Anhui Province, and the University of Science and Abilities of China Analysis Funds of the Double First-Class Initiative.