“Animals vaccinated with the mosaic-8 nanoparticles elicited antibodies that identified close to every SARS-like betacoronavirus stress we evaluated,” says Caltech postdoctoral pupil Alexander Cohen (PhD ’21), co-first creator of the contemporary seek.
A brand contemporary vogue of vaccine gives protection in opposition to a diversity of SARS-like betacoronaviruses, including COVID-19 variants, in mice and monkeys, constant with a up to date seek by Caltech.
Betacoronaviruses, including these that precipitated the SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 pandemics, are a impart vogue of coronaviruses that infect humans and animals. The contemporary vaccine works to induce the manufacturing of a large spectrum of harmful-reactive antibodies by presenting the immune machine with items of the spike proteins from SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) and 7 plenty of SARS-like betacoronaviruses, hooked up to a protein nanoparticle structure. Particularly, when vaccinated with this so-called mosaic nanoparticle, animal items relish been protected from an extra coronavirus, SARS-CoV, which modified into as soon as no longer truly appropriate one of the fundamental eight represented on the nanoparticle vaccine.
“Animals vaccinated with the mosaic-8 nanoparticles elicited antibodies that identified close to every SARS-like betacoronavirus stress we evaluated,” says Caltech postdoctoral pupil Alexander Cohen (PhD ’21), co-first creator of the contemporary study. “These sorts of viruses will be connected to the stress that causes the next SARS-like betacoronavirus outbreak, so what we if truth be told want would be something that targets this entire community of viruses. We have confidence now we relish that.”
The study modified into as soon as published on July 5 in a paper within the journal Science. The seek led by researchers within the laboratory of Caltech’s Pamela Bjorkman, the David Baltimore Professor of Biology and Bioengineering.
“SARS-CoV-2 has confirmed itself capable of making contemporary variants that would prolong the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic,” says Bjorkman, who will be a Merkin Institute Professor and govt officer for Biology and Biological Engineering. “In addition, the fact that three betacoronaviruses—SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2—relish spilled over into humans from animal hosts within the closing 20 years illustrates the need for making broadly keeping vaccines.”
In step with Bjorkman, such large protection is wanted “because we are capable of’t predict which virus or viruses amongst the immense numbers in animals will evolve in due path to infect humans to trigger but some other epidemic or pandemic. What we’re in search of to attain is form an all-in-one vaccine keeping in opposition to SARS-like betacoronaviruses no matter which animal viruses could maybe perchance evolve to enable human an infection and spread. This draw of vaccine would also defend in opposition to contemporary and future SARS-CoV-2 variants with out the need for updating.”
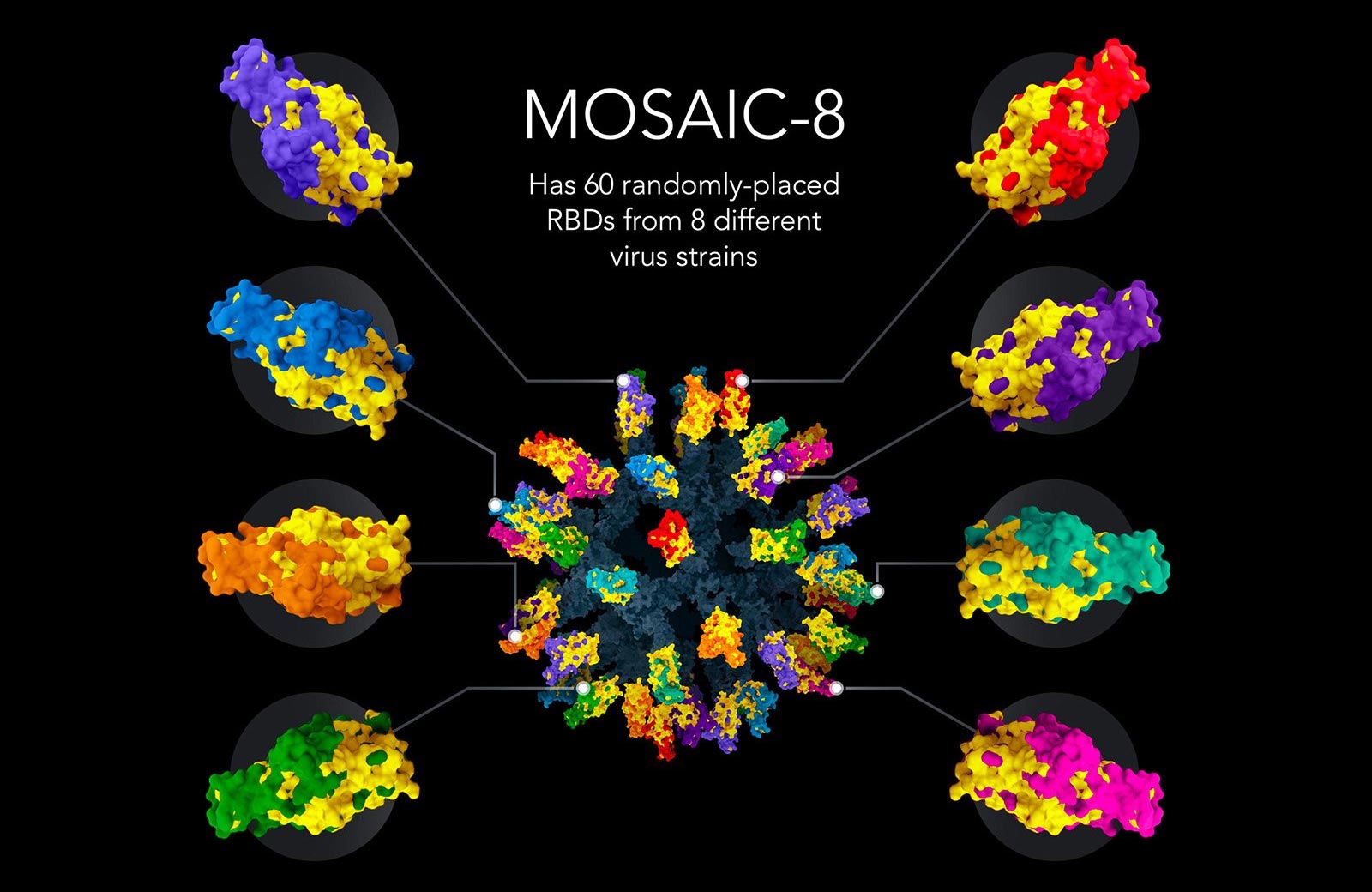
How it if truth be told works: A vaccine composed of spike domains from eight plenty of SARS-like coronavirusesThe vaccine know-how to join items of an endemic to protein nanoparticles modified into as soon as developed before the entirety by collaborators on the University of Oxford. The premise of the know-how is a little cage-like structure (a “nanoparticle”) made up of proteins engineered to relish “sticky” appendages on its surface, upon which researchers can join tagged viral proteins. These nanoparticles could maybe perchance additionally be prepared to demonstrate items of 1 virus easiest (“homotypic” nanoparticles) or items of plenty of plenty of viruses (“mosaic” nanoparticles). When injected into an animal, the nanoparticle vaccine items these viral fragments to the immune machine. This induces the manufacturing of antibodies, immune machine proteins that recognize and battle off impart pathogens, to boot to cell immune responses involving T lymphocytes and innate immune cells.
On this study seek, the scientists selected eight plenty of SARS-like betacoronaviruses—including SARS-CoV-2, the virus that has precipitated the COVID-19 pandemic, along with seven connected animal viruses that would relish doable to initiate an epidemic in humans—and hooked up fragments from these eight viruses onto the nanoparticle scaffold. The group selected impart fragments of the viral constructions, called receptor-binding domains (RBDs), that are serious for coronaviruses to enter human cells. In level of fact, human antibodies that neutralize coronaviruses essentially target the virus’s RBDs.
The premise is that such a vaccine could maybe perchance well induce the body to build antibodies that broadly recognize SARS-like betacoronaviruses to battle off variants to boot to those provided on the nanoparticle by focusing on frequent traits of viral RBDs. This build comes from the premise that the diversity and bodily association of RBDs on the nanoparticle will level of curiosity the immune response in opposition to aspects of the RBD that are shared by the entire SARS family of coronaviruses, thus achieving immunity to all. The info reported in Science on the current time demonstrates the aptitude efficacy of this formulation.
This infographic illustrates the contemporary vaccine, composed of RBDs from eight plenty of viruses. The desk reveals the large spectrum of SARS-CoV-2 variants and connected coronaviruses that the vaccine induces protection in opposition to. Credit score: Courtesy of Wellcome Soar, Caltech, and Merkin Institute
Designing experiments to measure the vaccine’s protection in miceThe resulting vaccine (here dubbed mosaic-8) is composed of RBDs from eight coronaviruses. Previous experiments led by the Bjorkman lab showed that mosaic-8 induces mice to build antibodies that react to a diversity of coronaviruses in a lab dish (Cohen et al., 2021, Science). Led by Cohen, the contemporary seek aimed to originate from this study to see if vaccination with the mosaic-8 vaccine could maybe perchance well induce keeping antibodies in a dwelling animal upon pronounce (in plenty of words, an infection) with SARS-CoV-2 or SARS-CoV.
The scientists aimed to review how essential protection in opposition to an infection modified into as soon as provided by a nanoparticle covered in plenty of coronavirus fragments (mosaic-8) versus a nanoparticle covered in easiest fragments of SARS-CoV-2 (a “homotypic” nanoparticle).
Three sets of experiments relish been conducted on mice. In one, the regulate, they inoculated mice with perfect the bare nanoparticle cage structure with out any virus fragments hooked up. A second community of mice relish been every injected with a homotypic nanoparticle covered easiest in SARS-CoV-2 RBDs, and a third community modified into as soon as injected with mosaic-8 nanoparticles. One experimental goal modified into as soon as to see if inoculation with mosaic-8 would defend the animals in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 to the identical degree because the homotypic SARS-CoV-2-immunized animals; a second goal modified into as soon as to review protection from a so-called “mismatched virus”—particular person that modified into as soon as no longer represented by an RBD on the mosaic-8 nanoparticle.
Particularly, the eight lines of coronavirus overlaying the mosaic nanoparticle intentionally did no longer consist of SARS-CoV, the virus that precipitated the distinctive SARS pandemic within the early 2000s. Thus, the group aimed to also review the degree of protection in opposition to a pronounce with the distinctive SARS-CoV virus, utilizing it to symbolize an unknown SARS-like betacoronavirus that would spill over into humans.
The mice aged within the experiments relish been genetically engineered to impart the human ACE2 receptor, which is the receptor on human cells that is aged by SARS-CoV-2 and connected viruses to build entry into cells all the draw via an infection. On this animal pronounce model, unvaccinated mice die if contaminated with a SARS-like betacoronavirus, thus offering a stringent test to review the aptitude for defense from an infection and illness in humans.
Mosaic vaccine protects mice in opposition to a identical SARS-like betacoronavirusAs anticipated, mice inoculated with the bare nanoparticle structure did die when contaminated with SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-2. Mice that relish been inoculated with a homotypic nanoparticle easiest coated in SARS-CoV-2 RBDs relish been protected in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 an infection nonetheless died upon exposure to SARS-CoV. These outcomes imply that contemporary homotypic SARS-CoV-2 nanoparticle vaccine candidates being developed in other areas would be effective in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 nonetheless also can no longer defend broadly in opposition to plenty of SARS-like betacoronaviruses crossing over from animal reservoirs or in opposition to future SARS-CoV-2 variants.
On the opposite hand, the entire mice inoculated with mosaic-8 nanoparticles survived both the SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV challenges with out a weight loss or plenty of great pathologies.
Nonhuman primate study also confirms the mosaic vaccine’s efficacyThe group then performed identical pronounce experiments in nonhuman primates, this time utilizing essentially the most promising vaccine candidate, mosaic-8, and evaluating the effects of mosaic-8 vaccination versus no vaccination in animal pronounce study. When inoculated with mosaic-8, the animals showed tiny to no detectable an infection when exposed to SARS-CoV-2 or SARS-CoV, as soon as more demonstrating the aptitude for the mosaic-8 vaccine candidate to be keeping for contemporary and future variants of the virus inflicting the COVID-19 pandemic to boot to in opposition to doable future viral spillovers of SARS-like betacoronaviruses from animal hosts.
Importantly, in collaboration with virologist Jesse Bloom (PhD ’07) of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Heart, the group chanced on that antibodies elicited by mosaic-8 focused essentially the most traditional parts of the RBDs all the draw in which via a various role of plenty of SARS-like betacoronaviruses—the so-called “conserved” half of the RBD—thus offering evidence for the hypothesized mechanism whereby the vaccine would be effective in opposition to contemporary variants of SARS-CoV-2 or animal SARS-like betacoronaviruses. By distinction, homotypic SARS-CoV-2 nanoparticle injections elicited antibodies in opposition to mainly stress-impart RBD regions, suggesting a majority of these vaccines would seemingly defend in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 nonetheless no longer in opposition to newly increasing variants or doable emerging animal viruses.
As a subsequent step, Bjorkman and colleagues will review mosaic-8 nanoparticle immunizations in humans in a Section 1 medical trial supported by the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Initiative (CEPI). To organize for the medical trial, which will largely join of us which relish been vaccinated and/or beforehand contaminated with SARS-CoV-2, the Bjorkman lab is planning preclinical animal model experiments to review immune responses in animals beforehand vaccinated with a up to date COVID-19 vaccine to responses in animals that are immunologically naïve with admire to SARS-CoV-2 an infection or vaccination.
“We relish talked concerning the need for diversity in vaccine pattern for the reason that very starting of the pandemic,” says Dr. Richard J. Hatchett, CEO of CEPI. “The breakthrough exhibited within the Bjorkman lab seek demonstrates large doable for a skill that pursues a up to date vaccine platform altogether, potentially overcoming hurdles created by contemporary variants. I’m tickled to recount that CEPI will be supporting this novel technique to pandemic prevention in Section I medical trials. The accelerated tempo the seek accomplished after receiving Wellcome Soar funding facilitated our relationship with them on the current time. The non-human primate data is amazingly encouraging and we’re enraged to toughen the next section of trials.”
Reference: “Mosaic RBD nanoparticles defend in opposition to pronounce by diverse sarbecoviruses in animal items” by Alexander A. Cohen, Neeltje van Doremalen, Allison J. Greaney, Hanne Andersen, Ankur Sharma, Tyler N. Starr, Jennifer R. Keeffe, Chengcheng Fan, Jonathan E. Schulz, Priyanthi N. P. Gnanapragasam, Leesa M. Kakutani, Anthony P. West, Greg Saturday, Yu E. Lee, Han Gao, Claudia A. Jette, Mark G. Lewis, Tiong K. Tan, Alain R. Townsend, Jesse D. Bloom, Vincent J. Munster and Pamela J. Bjorkman, 5 July 2022, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.abq0839
Wellcome Soar provided serious funding at a necessary time to tempo up the enchancment of the Caltech know-how, shortening the timeline to attain Section 1 medical trials by bigger than 18 months. Regina E. Dugan (PhD ’93), CEO of Wellcome Soar, says, “This early transition success demonstrates the worth of worldwide partnerships working collaboratively and with the urgency wanted to tackle future pandemic dangers.”
The paper is titled “Mosaic RBD nanoparticles defend in opposition to pronounce by diverse sarbecoviruses in animal items.” Neeltje van Doremalen of the Nationwide Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (Nationwide Institutes of Health) Rocky Mountain Laboratories is a co-first creator along with Cohen.
Extra Caltech co-authors are Jennifer Keeffe, study scientist; Chengcheng Fan, postdoctoral pupil study associate in Biology and Biological Engineering; Priyanthi Gnanapragasam, study technician; broken-down study technician Leesa Kakutani; Anthony P. West Jr., senior study specialist; broken-down study technician Yu Lee; Han Gao, study technician; and broken-down graduate student Claudia Jette (PhD ’22).
Other co-authors are Allison Greaney, Tyler Starr, and Jesse Bloom of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Heart; Hanne Andersen, Ankur Sharma, and Mark Lewis of BIOQUAL; Jonathan Schulz, Greg Saturday, and Vincent Munster of the Rocky Mountain Nationwide Laboratories; and Tiong Tan and Alain Townsend of the University of Oxford.
This preclinical vaccine validation seek modified into as soon as funded by Wellcome Soar, and constructed at as soon as on preliminary pattern and proof-of-belief study funded early within the pandemic by Caltech’s Merkin Institute for Translational Remedy. Other ongoing coronavirus work within the Bjorkman community is supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and George Mason Expeditiously Grants.