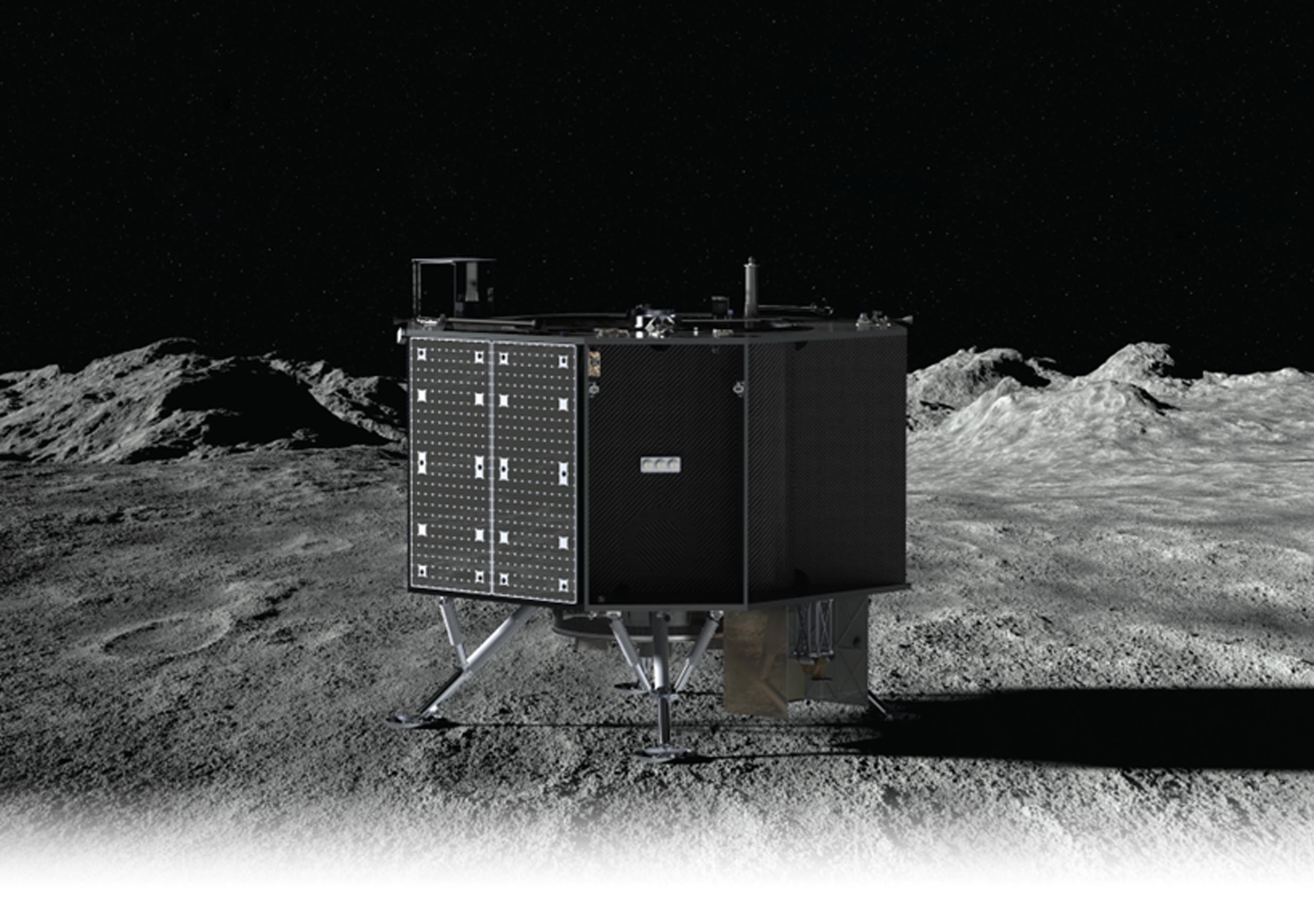
An illustration of Draper’s SERIES-2 lunar lander, which will disclose science and expertise payloads to the Moon for NASA in 2025. Credit score: Draper
Draper of Cambridge, Massachusetts has been given a contract by NASA to send Artemis scientific missions to the Moon in 2025. The business shipping is a component of NASA’s Artemis Industrial Lunar Payload Products and services (CLPS) program.
Draper is to blame for cease-to-cease shipping services and products, including payload integration, transport from Earth to the Moon’s flooring, and payload operations. Draper will get $73 million for the deal. This award marks the eighth flooring shipping task award issued to a CLPS vendor.
“This lunar flooring shipping to a geographic impart on the Moon that just isn’t visible from Earth will allow science to be conducted at a location of curiosity nonetheless a ways from the first Artemis human touchdown missions,” acknowledged Joel Kearns, deputy companion administrator for exploration in NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. “Working out geophysical process on the a ways aspect of the Moon will give us a deeper knowing of our solar system and present recordsdata to lend a hand us put together for Artemis astronaut missions to the lunar flooring.”
Schrödinger Basin, a large lunar affect crater on the a ways aspect of the Moon, not a ways from the lunar South Pole, is the vacation space of the experiments that will scurry aboard Draper’s SERIES-2 lander. This inviting geological location has a diameter of around 200 miles (320 kilometers). The interior ring of the basin is important for its gentle flooring deposits, that will per chance properly be a mix of both affect soften and volcanic self-discipline fabric, whereas the outer ring is made up of affect soften meteorites.
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter captured this image of Schrödinger basin, a large crater conclude to the south pole on the lunar a ways aspect. Credit score: NASA/LRO/Ernie Wright
“The payload shipping location is a first for us. Operations from the a ways aspect of the Moon will lend a hand toughen how we observe actions from this location to address scientific targets – all while we rep recordsdata from the payloads,” acknowledged Chris Culbert, CLPS program supervisor at NASA’s Johnson Rental Center in Houston. “The vendor-offered services and products will put together for future, more advanced lunar flooring operations.”
Schrödinger Basin is judicious one of the youngest affect basins on the lunar flooring whose affect uplifted the deep crust and higher mantle of the Moon in its peak ring. Later, a large volcanic eruption took impart within the interior basin. Researchers hope to survey the thermal and geophysical properties of the lunar interior as properly as electric and magnetic properties in a touchdown location that is protected in opposition to Earth’s electromagnetic fields.
Two of the three investigations selected for this flight are a part of NASA’s Payloads and Study Investigations on the Floor of the Moon (PRISM) demand proposals. Draper will disclose the three investigations that will collectively weigh about 209 pounds (95 kilograms) in mass and consist of the Farside Seismic Suite (FSS), which objectives to realize lend a hand NASA’s first lunar seismic recordsdata from the a ways aspect of the Moon. This original recordsdata could lend a hand scientists better perceive tectonic process on this impart of the Moon, demonstrate how on the total the lunar a ways aspect is impacted by diminutive meteorites, and present original recordsdata on the interior structure of the Moon. The instrument includes the two most comely seismometers ever built for spaceflight. FSS is judicious one of two PRISM selections. It is funded thru NASA in collaboration with the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES) – the French Rental Company – and is led by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.The Lunar Interior Temperature and Provides Suite (LITMS), moreover a PRISM option, is a suite of two devices: the Lunar Instrumentation for Thermal Exploration with Rapidity, a subsurface warmth-rush probe and pneumatic drill; and the Lunar Telluric Currents, an electrical self-discipline instrument. This payload suite objectives to investigate the warmth rush and subsurface electrical conductivity structure of the lunar interior in Schrödinger Basin. The aggregate of these measurements is a skill to acquire to the bottom of thermal and compositional structure of the flooring of the Moon. LITMS is funded by NASA and is led by the Southwest Study Institute.The Lunar Floor ElectroMagnetics Experiment (LuSEE), which will accomplish comprehensive measurements of electromagnetic phenomena on the flooring of the Moon. LuSEE makes expend of DC electric and magnetic self-discipline measurements to survey the must haves that retain watch over the electrostatic doable of the lunar flooring, which, in flip, plays a controlling characteristic in mud transport. LuSEE moreover makes expend of plasma wave measurements to picture the lunar ionosphere and the interaction of the solar wind and magnetospheric plasma with the lunar flooring and crustal magnetic fields. As properly as, this payload will accomplish comely radio frequency measurements to measure solar and planetary radio emissions. LuSEE is funded by NASA in collaboration with CNES, and is led by University of California, Berkeley’s Rental Science Laboratory.A pair of business deliveries continue to be a part of NASA’s plans on the Moon. Future payloads delivered with CLPS could consist of more science experiments, including expertise demonstrations that toughen for the agency’s Artemis missions. Through Artemis, NASA will land the first woman and the first particular person of coloration on the Moon, paving the model for a lengthy-length of time, sustainable lunar presence and serving as a stepping stone for future astronaut missions to Mars. Artemis I is scheduled to starting up no sooner than August 29, 2022, with a subsequent take a look at flight with crew scheduled to happen in 2024 upfront of NASA sending humans to the flooring of the Moon no sooner than 2025.