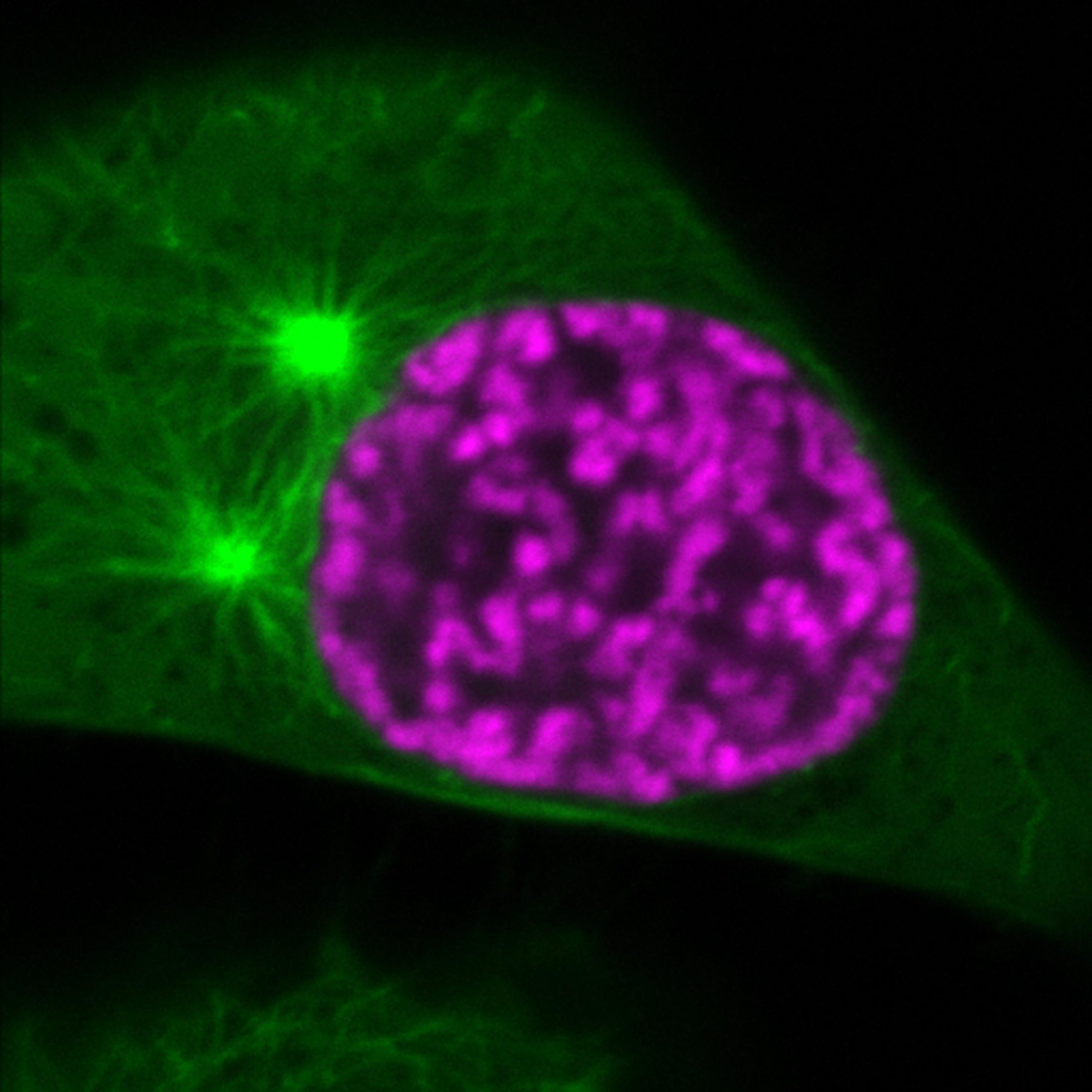
Organization of mitotic chromosomes (magenta) and spindle microtubules (green) at an early section of cell division. Rapidly after what’s confirmed within the image, the microtubules will invade the nuclear dwelling. Nevertheless, chromatin compaction regulated by histone acetylation will prevent the perforation of the chromosomes by microtubules. Credit score: ©Gerlich/IMBA
How the genome is packed into chromosomes that might perchance well well be faithfully moved at some level of cell division.
Scientists discovered a molecular mechanism that confers particular bodily properties to chromosomes in dividing human cells to permit their devoted transport to the progeny. The research crew showed how a chemical modification establishes a entertaining flooring boundary on chromosomes, thus permitting them to withstand perforation by microtubules of the spindle equipment. The researchers are from the Gerlich Crew at IMBA – Institute of Molecular Biotechnology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, and their findings are published this day (August 3, 2022) within the journal Nature.
Precisely one genome reproduction prefer to be transported to every of the two daughter cells at some level of cell division. Faithful genome segregation requires the packaging of extraordinarily long chromosomal DNA molecules into discrete our bodies. This permits them to be efficiently moved by the mitotic spindle, a filament machine silent of hundreds of microtubules. The recent findings by the Gerlich Look at Crew at IMBA – Institute of Molecular Biotechnology of the Austrian Academy of Sciences – shed gentle on how mitotic chromosomes withstand the fixed pushing and pulling forces generated by the microtubules. “Amidst this complicated machine, the determined bodily properties are conferred to the chromosomes by changing the levels of histone acetylation, a chemical modification at some level of the chromatin fiber,” says IMBA Crew Leader Daniel Gerlich.
Prior research had demonstrated that, in dividing cells, the chromatin fibers are folded into loops by a substantial protein complicated known as condensin. Nevertheless, the characteristic of condensin on my own might perchance well well now not ticket why chromosomes seem as dense our bodies with a entertaining flooring rather then a free construction comparable to a bottlebrush. Some reviews had urged a characteristic of histone acetylation in regulating the extent of compaction at some level of cell division, but the interaction of histone acetylation with condensin and its purposeful relevance remained unclear. “With our work, we are in fact ready to conceptually disentangle the two mechanisms,” states Gerlich.
The scientists varied the levels of condensin and histone acetylation to survey their steady effects. Putting off condensin disrupted the elongated shape of chromosomes in dividing cells and lowered their resistance to pulling forces but did no longer occupy an mark on their level of compaction. Combining condensin depletion with a medicines that increases the levels of histone acetylation introduced on broad chromatin decompaction in dividing cells, and perforation of chromosomes by microtubules.
The crew hypothesized that chromatin is organized as a swollen gel at some level of a few the cell cycle (when it is somewhat highly acetylated) and that this gel compacts to an insoluble hold at some level of cell division when the acetylation levels globally lower. They then developed an assay to probe the solubility of chromatin by fragmenting mitotic chromosomes into itsy-bitsy devices. The fragments of mitotic chromosomes formed droplets of liquid chromatin, but when the acetylation level used to be increased, the chromatin fragments dissolved within the cytoplasm. These observations enhance a mannequin where a world low cost of chromatin acetylation at some level of mitosis establishes an immiscible chromatin gel with a entertaining section boundary, providing a bodily foundation for resistance in opposition to microtubule perforation.
With extra experiments interesting pure chromatin that used to be reconstituted in vitro, and by probing chromatin access by varied soluble macromolecules, the researchers discovered that immiscible chromatin kinds a construction dense in detrimental fee that excludes negatively charged macromolecules and microtubules.
“Our survey reveals how DNA looping by the condensin complicated cooperates with a chromatin section separation job to derive mitotic chromosomes that withstand both pulling and pushing forces exerted by the spindle. The deacetylation of histones at some level of cell division hence confers queer bodily properties to chromosomes that are required for his or her devoted segregation,” concludes Daniel Gerlich.
Reference: “A mitotic chromatin section transition prevents perforation by microtubules” 3 August 2022, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05027-y
Funding: Austrian Science Fund, Vienna Science and Technology Fund, Vienna Science and Technology Fund, Howard Hughes Scientific Institute, NIH/Nationwide Institutes of Well being, Welch Foundation, Boehringer Ingelheim Fonds