A pair of UCLA bioengineers and a former postdoctoral scholar accept as true with developed a brand unique class of bionic 3D camera programs that would perhaps well mimic flies’ multiview imaginative and prescient and bats’ pure sonar sensing, ensuing in multidimensional imaging with out of the ordinary depth range that would perhaps well perhaps furthermore scan thru blind spots.
Powered by computational picture processing, the camera can decipher the scale and shape of objects hidden spherical corners or gradual different items. The technology would perhaps well perhaps be incorporated into self reliant automobiles or scientific imaging instruments with sensing capabilities a ways past what’s conception of insist of the work currently. This study has been published in Nature Communications.
At hour of darkness, bats can visualize a absorbing picture of their surroundings by the utilization of a assemble of echolocation, or sonar. Their high-frequency squeaks soar off their surroundings and are picked relief up by their ears. The minuscule variations in how lengthy it takes for the echo to attain the nocturnal animals and the intensity of the sound characterize them in exact time the put issues are, what’s in the methodology and the proximity of doable prey.
Many bugs accept as true with geometric-fashioned compound eyes, in which every “gaze” is gentle of quite a bit of to tens of hundreds of individual items for scrutinize—making it which that you may perhaps contemplate to gape the the same part from a pair of lines of scrutinize. Let’s assume, flies’ bulbous compound eyes give them a attain-360-stage quiz even supposing their eyes accept as true with a mounted focal point length, making it complicated for them to gape the relaxation a ways away, equivalent to a flyswatter held aloft.
Inspired by these two pure phenomena existing in flies and bats, the UCLA-led crew put of living out to assemble a high-efficiency 3D camera gadget with evolved capabilities that leverage these advantages but moreover contend with nature’s shortcomings.
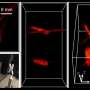
“Whereas the basis itself has been tried, seeing across a unfold of distances and spherical occlusions has been a prime hurdle,” mentioned glance chief Liang Gao, an partner professor of bioengineering at the UCLA Samueli Faculty of Engineering. “To address that, we developed a novel computational imaging framework, which for the first time permits the acquisition of a big and deep panoramic quiz with straight forward optics and a minute array of sensors.”
Called “Compact Gentle-discipline Photography,” or CLIP, the framework permits the camera gadget to “see” with an prolonged depth range and spherical objects. In experiments, the researchers demonstrated that their gadget can “see” hidden objects which would perhaps well perhaps be not spotted by former 3D cameras.
The researchers also expend a assemble of LiDAR, or “Gentle Detection And Ranging,” in which a laser scans the surroundings to assemble a 3D plot of the put.
Venerable LiDAR, with out CLIP, would enlighten a high-resolution snapshot of the scene but hotfoot away out hidden objects, very like our human eyes wo