May 23, 2023– Imagine a day when an easy injection triggers a damaged bone to recover. When small, ingestible gadgets stick around in the body, undetected, tracking our health or providing life-saving medications. When brain and heart implants fit together with flesh so effortlessly that the body believes they’ve existed the whole time.
These are the imagine products researchers who have actually worked for years to simulate the complex architecture of the body in hopes of changing damaged parts or dealing with illness.
The issue, state bioengineers, is that a lot of replacement and restorative parts– from prosthetics to pacemakers– are made from difficult, dry, lifeless products, like metal or plastic, while biological tissue is soft, damp, and living.
The body understands the distinction and tends to decline replicas.
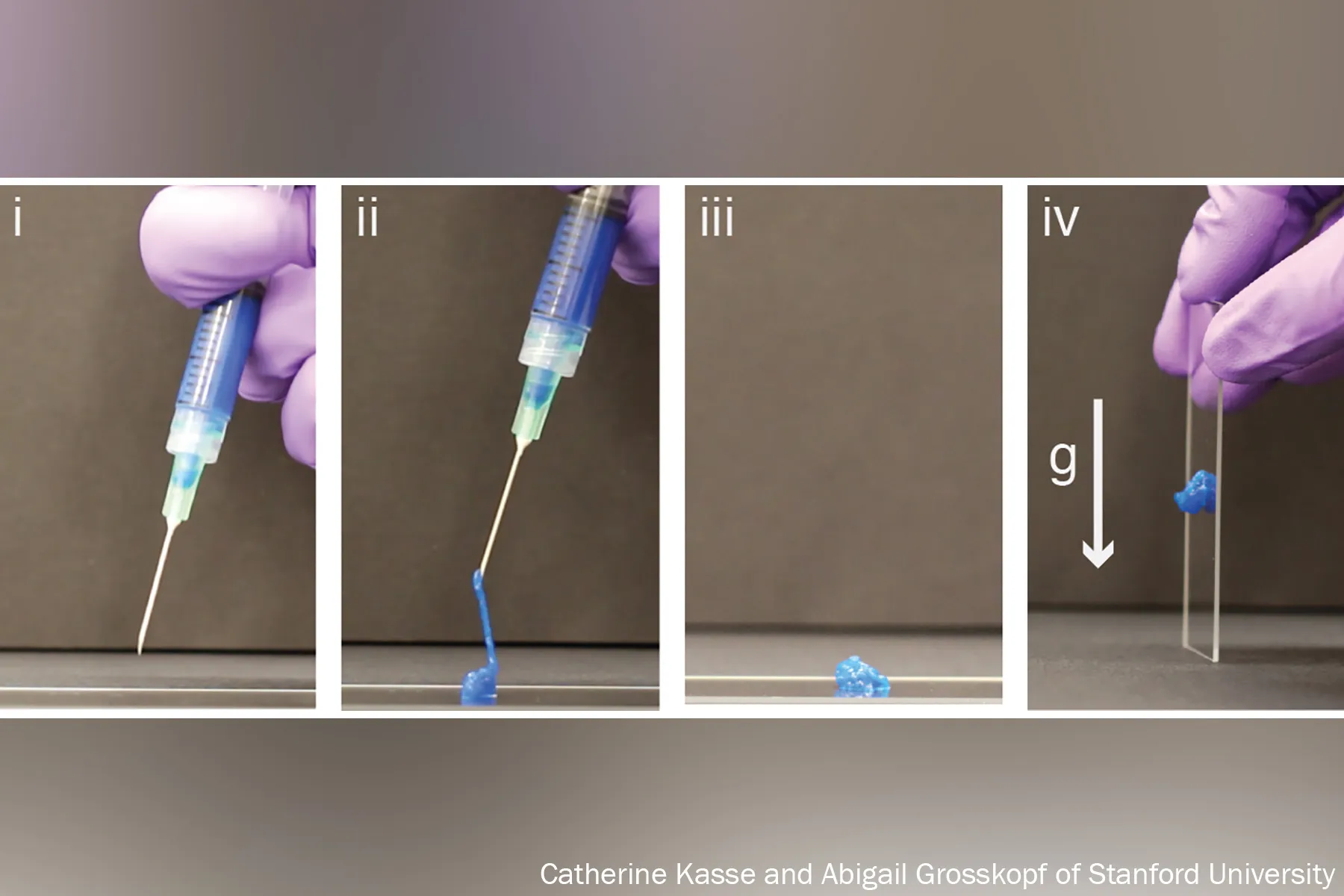
Get in hydrogels, three-dimensional networks of particles inflamed with– by meaning– water.
Explained in 1960 by developers of soft contact lenses, these odd, shape-shifting compounds are able to change from liquid to strong to a squishy in-between. (Early, basic usages consist of hair gel or Jell-O.). Slow to get attention, growing to simply 1,000 research studies released by 1982, they’ve ended up being the topic of extreme research study just recently, with 100,000 documents overall released by 2020, and 3,800 currently this year alone.
As chemists, biologists, and engineers start to work more with one another and with medical physicians, the blossoming hydrogel field is poised to change the method we take medication and deal with damaged joints and lead the way for a relatively sci-fi future in which organs, consisting of brains, can engage straight with makers.
“We are, basically, hydrogels,” stated Benjamin Wiley, PhD, a chemistry teacher at Duke University in Durham, NC. “As individuals establish brand-new hydrogels that more carefully match the tissues in our body, we’ll have the ability to deal with an entire host of conditions we could not deal with in the past.”
From Contact Lenses to Brain Implants
Simply put, a hydrogel resembles a mesh bag of water.
The mesh is made from polymers, or spaghetti-like hairs of particles, sewn together in a duplicating pattern and inflamed with H2O, similar to the method 3D matrixes in our body surround, assistance, and offer structure to our cells and tissues.
“Imagine a soccer internet, with all of these long fibers woven together to develop the internet,” stated Eric Appel, PhD, an associate teacher of products science and engineering at Stanford University.
While the more comprehensive classification of “gels” might be filled with anything, consisting of chemical solvents, water is the essential active ingredient that sets hydrogels apart, making them perfect for, as some researchers put it, “combining human beings and makers.”
Human bones have to do with 25% water, while muscles hover around 70% and the brain is 85%. The valuable liquid plays a host of vital functions, from shuttling nutrients in and squander out to assisting cells talk with each other.
Lab-made hydrogels can be packed with freight (like a ball in the web), consisting of cells or drugs that assist imitate a few of those functions.
Hydrogels are likewise soft and flexible like flesh. If utilized in implants, they might be less most likely to harm surrounding tissue.
“Think about a metal spoon in your bowl of pudding. As you’re shaki