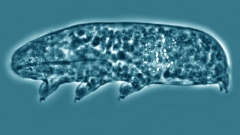
Biologists have actually explained 2 brand-new tardigrade genera and associated types– 2 of which are brand-new to science– from the mountain glaciers of New Zealand’s Southern Alps.
Kopakaius nicolae Scale bar– 50 µm. Image credit: Zawierucha et al, doi: 10.1016/ j.ympev.2022107634
First found in 1773, tardigrades (phylum Tardigrada) are a varied group of tiny invertebrates with 8 legs and body size varying from 50 -1,200 µm (micrometers).
Also called water bears or moss piglets, these animals can live for approximately 60 years and are popular for their capability to endure severe conditions.
They have the ability to endure for as much as 30 years without food or water, for a couple of minutes at temperature levels as low as minus 272 degrees Celsius (minus 457 degrees Fahrenheit) or as high as 150 degrees Celsius (302 degrees Fahrenheit), and minus 20 degrees Celsius (minus 4 degrees Fahrenheit) for years.
They stand up to pressures from practically 0 atm in area as much as 1,200 atm at the bottom of the Marianas Trench, and are likewise resistant to radiation levels approximately 5,000 -6,200 Gy.
Tardigrades populate numerous limno-terrestrial (soil, bryophythes, lichens, algae mats) and marine (sediments, plants) environments, from polar to tropical areas and from high mountains peaks to deep oceans.
Due to their tolerance to undesirable ecological conditions, tiny size and long-range dispersal abilities, they are cosmopolitan and live in remote and frequently hostile environments.
Although tardigrades are well studied worldwide, their variety and ecology in cold environments stay badly acknowledged in spite of their essential functions in trophic webs and community function.
The richness of tardigrade types in severe glacial environments is reasonably low compared to that of surrounding communities, likely due to strong choice pressures consisting of completely low temperature levels, high irradiation, and regular freezing.
Importantly, glacier tardigrades are mainly unique from their limno-terrestrial equivalents, as evidenced by DNA and/or phenotypic significant difference.
Kararehius gregorii Scale bar– 50 µm. Image credit: Zawierucha et al, doi: 10.1016/ j.ympev.2022107634
” We explain 2 brand-new genera of tardigrades from the build-up zones of 3 New Zealand glaciers by an integrative taxonomic technique integrating morphological, morphometric and hereditary information,” stated lead author Dr. Krzysztof Zawierucha, a scientist in the Department of Animal Taxonomy and Ecology at Adam Mickiewicz University and the Faculty of Forestry and Wood Sciences at the Czech University of Life Sciences Prague, and his coworkers from Poland, New Zealand and the United