(opens in contemporary tab)
Researchers delight in stumbled on never-sooner than-viewed varieties of crystal hidden in little grains of completely preserved meteorite mud. The mud became left in the support of by an enormous set up rock that exploded over Chelyabinsk, Russia, 9 years previously.
On Feb. 15, 2013, an asteroid measuring 59 toes (18 meters) all over and weighing 12,125 a lot (11,000 metric a lot) entered Earth‘s ambiance at around 41,600 mph (66,950 km/h). Fortuitously, the meteor exploded around 14.5 miles (23.3 kilometers) above the city of Chelyabinsk in southern Russia, showering the encompassing set up in little meteorites and fending off a tall single collision with the ground. Experts on the time described the event as a predominant be-cautious name to the risks asteroids pose to the planet.
The Chelyabinsk meteor explosion became the best of its form to happen in Earth’s ambiance since the 1908 Tunguska event. It exploded with a power 30 cases greater than the atomic bomb that rocked Hiroshima, fixed with NASA (opens in contemporary tab). Video photos (opens in contemporary tab) of the event showed the set up rock burning up in a flash of light that became temporarily brighter than the sun, sooner than constructing a highly efficient sonic insist that broke glass, broken constructions and injured around 1,200 folk in the city below, fixed with Dwell Science’s sister online page Residence.com (opens in contemporary tab).
In a brand contemporary stare, researchers anlyzed one of the most little fragments of set up rock that had been left in the support of after the meteor exploded, known as meteorite mud. On the total, meteors make a limited quantity of mud as they burn up, but the little grains are lost to scientists on myth of they are either too limited to procure, scattered by the wind, tumble into water or are spoiled by the ambiance. Nonetheless, after the Chelyabinsk meteor exploded, an enormous plume of mud hung in the ambiance for extra than four days sooner than in the damage raining down on Earth’s floor, fixed with NASA. And fortuitously, layers of snow that fell rapidly sooner than and after the event trapped and preserved some mud samples unless scientists could perhaps maybe well acquire better them rapidly after.
Linked: Diamond hauled from deep inside of Earth holds never-sooner than-viewed mineral
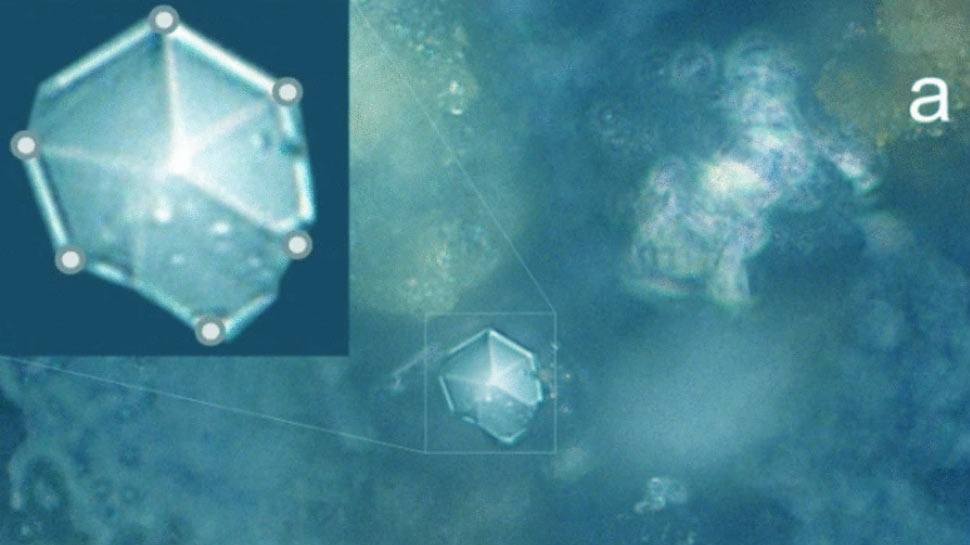
The researchers stumbled upon the contemporary varieties of crystal whereas they had been inspecting specks of the mud under a current microscope. This kind of little constructions, which became perfect correct substantial ample to seek info from under the microscope, became fortuitously in level of interest correct on the middle of 1 of the slides when one group member peered thru the eyepiece. If it had been wherever else the group would likely delight in neglected it, fixed with Sci-Recordsdata (opens in contemporary tab).
After examining the mud with extra highly efficient electron microscopes, the researchers stumbled on many extra of these crystals and examined them in great greater ingredient. Nonetheless, even then, “finding the crystals using an electron microscope became quite aggravating attributable to their limited size,” the researchers wrote of their paper, which became printed Would possibly perhaps maybe also 7 in The European Physical Journal Plus (opens in contemporary tab).
(opens in contemporary tab)
The contemporary crystals came in two certain shapes; quasi-spherical, or “almost spherical,” shells and hexagonal rods, each and every of that delight in been “phenomenal morphological peculiarities,” the researchers wrote in the stare.
Extra evaluation using X-rays printed that the crystals had been product of layers of graphite — a make of carbon product of overlapping sheets of atoms, commonly frail in pencils — surrounding a central nanocluster on the coronary heart of the crystal. The researchers imply that the most likely candidates for these nanoclusters are buckminsterfullerene (C60), a cage-fancy ball of carbon atoms, or polyhexacyclooctadecane (C18H12), a molecule product of carbon and hydrogen.
The group suspects that the crystals formed in the excessive-temperature and excessive-stress stipulations created by the meteor breaking up, even supposing the particular mechanism is serene unclear. Within the lengthy bound, the scientists hope to discover down diversified samples of meteorite mud from diversified set up rocks to seek info from if these crystals are a prime byproduct of meteor break-united states of americaor are phenomenal to the Chelyabinsk meteor explosion.
Before all the issues set up printed on Dwell Science.