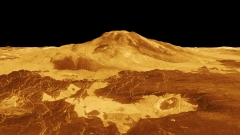
Massive worldwide volcanism that covered 80% of Venus’ surface area in lava might have been the choosing element that changed Venus from a damp and moderate world into the suffocating, sulfuric, hellish world that it is today.
The surface area temperature level on Venus is a sweltering 867 degrees Fahrenheit (464 degrees Celsius), hot enough to melt lead, and there’s a squashing pressure of 90 environments beneath the thick clouds of co2 laced with wearing away sulfuric acid. Typically decried as Earth‘s “wicked twin,” Venus is a victim of a runaway greenhouse result, no doubt magnified by Venus having to do with 25 million miles (40 million kilometers) closer to the s un than Earth and for that reason getting more heat.
Yet, there’s growing proof that Venus wasn’t constantly by doing this, and might have as soon as been a temperate world rather comparable to Earth– maybe more just recently, in geological terms, than anticipated.
Related: NASA’s Parker Solar Probe records spectacular Venus picture throughout close flyby
Michael Way, of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Maryland, has actually led much of the research study establishing this brand-new vision of Venus. In their most current paper, he and his group argue that Venus’ volcanism might have eventually been what pressed the world over the edge by sending out large quantities of co2– as we understand, a powerful greenhouse gas– rippling into Venus’ environment
In the 1990 s, NASA’s Magellan spacecraft radar-mapped the surface area of Venus, which is otherwise obscured by the world’s thick environment, and discovered that much of the surface area was covered in volcanic basalt rock. Such “big igneous provinces” are the outcome of 10s of thousands, if not numerous countless years’ worth of huge volcanism that took place eventually in the previous billion years.
In specific, numerous of these occasions can be found in the area of a million years, maybe, and each covering numerous countless square miles or kilometers in lava, might have endowed Venus’ environment with a lot co2 that the environment would have been not able to cope. Any oceans would have boiled away, including wetness to the environment, and due to the fact that water vapor is likewise a greenhouse gas, speeding up the runaway greenhouse result. In time, the water would have been lost to area, however the co2, and the unwelcoming world, stayed.
” While we’re not yet sure how typically the occasions which produced these fields took place, we must have the ability to narrow it down by studying Earth’s own history,” Way stated in a declaration
The frequency with which huge volcanic occasions forming big igneous provinces have actually happened in the world suggests that it is most likely that numerous such occasions might have taken place on Venus within a million years. These occurrences might have scarred Venus permanently.
Earth itself has had some close calls. So-called “super-volcanoes” have actually been linked to various mass-extinction occasions in the world over the previous half-a-billion years. The Late Devonian period mass termination 370 million years earlier has actually been associated by some to super-volcanism in what is now Russia and Siberia, as well as to a different super-volcanic eruption in Australia. The Triassic– Jurassic mass termination is commonly blamed on the development of the greatest of Earth’s big igneous provinces, the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province, 200 million years earlier. Even the death of the dinosaurs 65 million years back might have been triggered by the double whammy of an asteroid strike and super-volcanism in the Deccan Traps, a big igneous province in India.
For unidentified factors, comparable volcanic occasions on Venus were far more extensive and prompted a runaway greenhouse result that changed the world. On Earth, the carbon-silicate cycle that acts as the world’s natural thermostat, exchanging carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases in between the mantle and the environment over millions of years, was able to avoid Earth from following the very same course as Venus.
Two future NASA objectives will venture to address a few of these concerns. DAVINCI, the Deep Atmosphere Venus Investigation of Noble Gases, Chemistry and Imaging objective will release later on this years, to be followed by VERITAS, the Venus Emissivity, Radio Science, InSAR, Topography and Spectroscopy objective in the early 2030 s. The European Space Agency’s EnVision objective likewise targets launch at some point in the 2030 s, while China has actually proposed a possible objective called VOICE, the Venus Volcano Imaging and Climate Explorer, that if introduced would reach Venus in 2027 to study the world’s environment and geology.
” A main objective of DAVINCI is to limit the history of water on Venus and when it might have vanished, supplying more insight into how Venus’ environment has actually altered gradually,” Way stated.
The findings were released in the Planetary Science Journal previously this year.
Follow Keith Cooper on Twitter @21 stCenturySETI. Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook