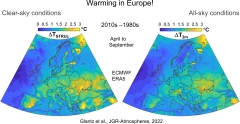
Left and best figures reveal warming in Europe of the summer season half-year throughout the most recent 4 years, partitioned for clear-sky and all.sky conditions, respectively. Credit: Paul Glantz/Stockholm University The warming throughout the summer season in Europe has actually been much faster than the worldwide average, reveals a brand-new research study released in the Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres. As a repercussion of human emissions of greenhouse gases, the environment throughout the continent has actually likewise ended up being drier, especially in southern Europe, resulting in even worse heat waves and an increased danger of fires. According to the UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), warming over acreage takes place considerably faster than over oceans, with 1.6 degrees Celsius and 0.9 degrees Celsius usually, respectively. It suggests that the international greenhouse gas emissions spending plan to remain under a 1.5-degree Celsius warming on land has actually currently been consumed. Now, a brand-new research study by scientists at Stockholm University reveals that the emissions spending plan to prevent a 2-degree Celsius warming over big parts of Europe throughout the summer season half-year (April-September) has actually likewise been consumed. Measurements expose that the warming throughout the summer season months in big parts of Europe throughout the last 4 years has actually currently exceeded 2 degrees Celsius. Left and best figures reveal modifications in practical and hidden heat fluxes, respectively, in Europe throughout the most recent 4 years of the summertime half year. Credit: Paul Glantz/Stockholm University “Climate modification is major as it causes, to name a few things, more regular heat waves in Europe. These, in turn, increase the threat of fires, such as the terrible fires in southern Europe in the summer season of 2022,” states Paul Glantz, Associate Professor at the Department of Environmental Science, Stockholm University, and primary author of the research study. In southern Europe, a clear, so-called, favorable feedback triggered by worldwide warming appears, i.e. warming is enhanced due to drier soil and reduced evaporation. There has actually been less cloud protection over big parts of Europe, most likely as an outcome of less water vapor in the air. “What we see in southern Europe remains in line with what IPCC has actually anticipated, which is that an increased human effect on the greenhouse result would result in dry locations in the world ending up being even drier,” states Paul Glantz. Left and best figures reveal reduction in clouds in Europe throughout the most recent 4 years, for the summertime half year, with regard to low level clouds and overall quantity of clouds throughout the environment, respectively. Credit: Paul Glantz/Stockholm University Impact of aerosol particlesThe research study likewise consists of an area about the approximated effect of aerosol particles on the temperature level boost. According to Paul Glantz, the fast warming in, for instance, Central and Eastern Europe, is very first and primary a repercussion of the human emissions of long-lived greenhouse gases, such as co2. Considering that emissions of temporary aerosol particles from, for example, coal-fired power plants have actually reduced considerably over the previous 4 years, the combined impact has actually led to a severe temperature level boost of over 2 degrees Celsius. Coal power plants in the world emit over 12 Gt of co2 each year, almost one-third of the overall emissions of co2. Coal power plants make up for that reason the single biggest source of worldwide warming. Coal power plants release likewise sulfur dioxide that forms aerosols in the environment. Coal power plants have actually reduced and increased significantly in Europe and East Asia, respectively, throughout the most recent 4 years. Credit: Tomasz Matuszewski/Mostphotos “The air-borne aerosol particles, prior to they started to reduce in the early 1980 s in Europe, have actually masked the warming triggered by human greenhouse gases by simply over one degree usually for the summer season half-year. As the aerosols in the environment reduced, the temperature level increased quickly. Human emissions of co2 are still the greatest risk as they impact the environment for hundreds to countless years,” states Paul Glantz. According to Paul Glantz, this impact offers a precursor of future warming in locations where aerosol emissions are high, such as in India and China. Warming and as a result drier conditions in Europe, especially for southern nations, greater the threat for fires. In the report “Spreading like wildfires: the increasing danger of remarkable landscape fires,” by UN Environmental Program (UNEP) and GRID-Arendal (a UNEP partner) in 2022, conclude that environment modification and land-use modification are making wildfires even worse. The report expects an international boost of severe fires, even in locations formerly untouched. https://www.unep.org/resources/report/spreading-wildfire-rising-threat-extraordinary-landscape-fires. Credit: Ryhor Bruyeu/Mostphotos Background truths– The greenhouse impact and aerosol effectFossil burning results in the release of both aerosol particles and greenhouse gases. Their source is typical, their impacts on environment vary. Paul Glantz, Associate Professor at the Department of Environmental Science, Stockholm University, and primary author of the research study. Credit: Stockholm University About the greenhouse result Greenhouse gases are mainly untouched by solar radiation while they soak up infrared radiation effectively, causing re-emission towards the Earth’s surface area. The Earth soaks up both solar radiation and infrared radiation, which causes the warming of the lower part of the environment in specific. Time-space: Greenhouse gases are normally long-lived in the environment and this uses above all to co2 where human emissions impact environment for hundreds to countless years. It likewise implies that greenhouse gases spread out equally over the whole world. About the aerosol impact In contrast to greenhouse gases, aerosol particles impact inbound solar radiation, i.e. they spread part of the sunshine back into area triggering a cooling impact. Human emissions of aerosol container boost this cooling impact. Time-space: Airborne human aerosol particles have a life time of about a week, which implies that they generally cool the environment in your area or regionally and in the short-term. According to the Paris Agreement, all celebrations need to dedicate to significantly lower their greenhouse gas emissions, however it is likewise crucial to reduce concentrations of aerosol particles too due to the fact that, in addition to their results on environment, aerosol particles in contaminated air cause roughly 8 million sudden deaths each year around the globe. Referral: “Unmasking the Effects of Aerosols on Greenhouse Warming Over Europe” by P. Glantz, O. G. Fawole, J. Ström, M. Wild and K. J. Noone, 4 November 2022, Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres. DOI: 10.1029/2021 JD035889 Funding: Svenska Forskningsrådet Formas (Formas)
Read More
Big Parts of Europe Warming Twice As Fast as the Planet– Already Surpassed 2 ° C