MIT engineers fabricate new surface therapies that plan water boil extra efficiently.
Unique surface therapies would perchance well per chance furthermore put energy for systems aged in quite lots of industries.At the coronary heart of a big sequence of industrial processes, including most electrical energy producing plant life, many chemical manufacturing systems, and even cooling systems for electronics, is an energy-intensive step with the boiling of water or different fluids.
They would well furthermore significantly lower their energy exhaust by bettering the efficiency of systems that warmth and evaporate water. MIT researchers gain now found a ability to raise out staunch that, with a specially designed surface medication for the supplies aged in these systems.
Three different forms of surface changes, at different size scales, together account for the increased efficiency. The brand new findings are described in a paper revealed in the journal Developed Provides by contemporary MIT graduate Youngsup Music PhD ’21, Ford Professor of Engineering Evelyn Wang, and 4 others at MIT. The scientists caution that this preliminary finding is mute at a laboratory scale, and extra effort is required to fabricate a purposeful, industrial-scale job.
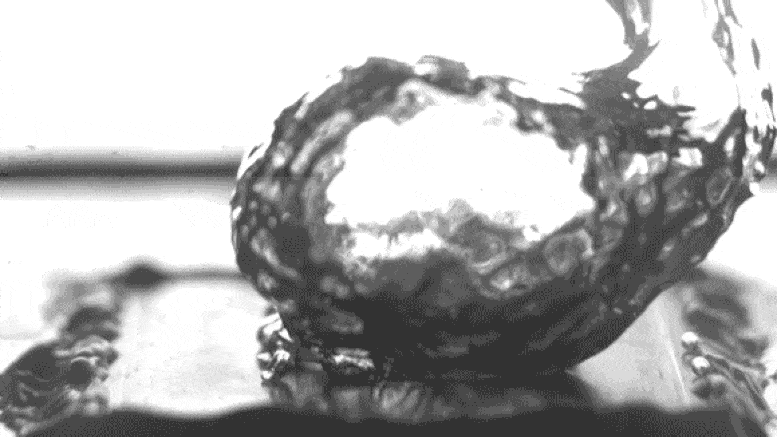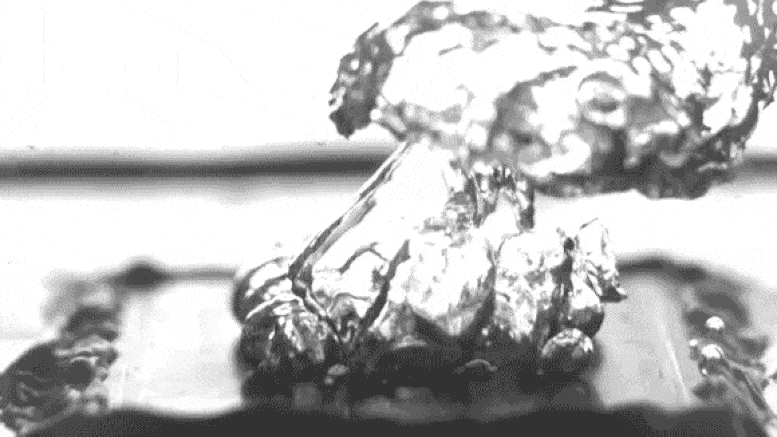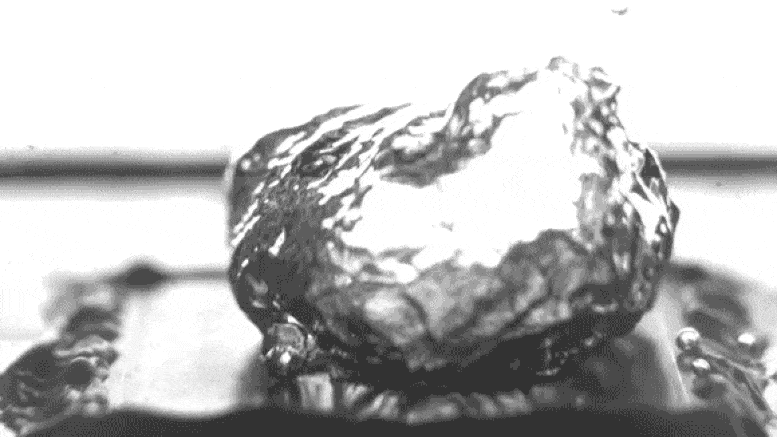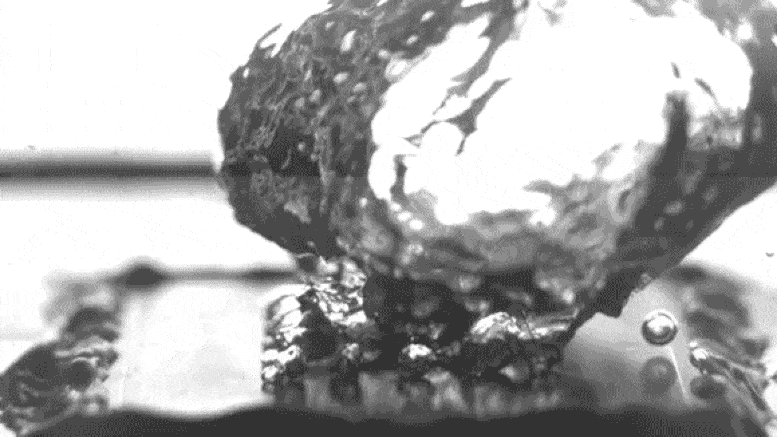
Excessive-sprint video of the researchers’ take a look at setup shows water boiling on a specially treated surface, which causes bubbles to fabricate at teach separate parts somewhat than spreading out in a film across the skin, thus leading to extra ambiance friendly boiling. The video has been slowed down by 100 times to level to extra detail. Credit: Courtesy of the researchers
The warmth switch coefficient (HTC) and the severe warmth flux (CHF) are two key parameters that reveal the boiling job. There’s generally a tradeoff between the 2 in supplies fabricate, so anything that improves certainly this kind of parameters tends to plan different worse. But both are critical for the efficiency of the gadget, and now, after years of work, by their combination of different textures added to a material’s surface, the personnel of scientists achieved a strategy of significantly bettering both properties at the identical time.
“Both parameters are critical,” Music says, “however bettering both parameters together is extra or less complex because they’ve intrinsic alternate-offs.” The placement off of that, he explains, is “because if now we gain hundreds bubbles on the boiling surface, that formulation boiling is terribly ambiance friendly, however if now we gain too many bubbles on the skin, they are going to coalesce together, that would perchance well per chance furthermore fabricate a vapor film over the boiling surface.” That film introduces resistance to the warmth switch from the brand new surface to the water. “If now we gain vapor in between the skin and water, that forestalls the warmth switch efficiency and lowers the CHF ticket,” he says.
Music, who is now a postdoctoral researcher at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, conducted powerful of the analysis as segment of his doctoral thesis work at MIT. Whereas different parts of the brand new surface medication he developed had been previously studied, the researchers screech this work is the foremost to level to that these programs would perchance well per chance furthermore very effectively be blended to conquer the tradeoff between the 2 competing parameters.
The predominant to the brand new surface medication is to add textures at several different size scales. Electron microscope photos level to millimeter-scale pillars and dents(first two photos), whose surfaces are lined with cramped nanometer-scale ridges (backside two photos) to lend a hand the efficiency of the boiling response. Credit: Courtesy of the researchers
Alongside with a series of microscale cavities, or dents, to a surface is a strategy of controlling the formulation bubbles fabricate on that surface, keeping them effectively pinned to the locations of the dents and combating them from spreading out into a warmth-resisting film. In this work, the researchers created an array of 10-micrometer-huge dents separated by about 2 millimeters to forestall film formation. But that separation also reduces the concentration of bubbles at the skin, that would perchance well per chance furthermore lower the boiling efficiency. To make amends for that, the personnel launched a powerful smaller-scale surface medication, organising cramped bumps and ridges at the nanometer scale, which increases the skin enlighten and promotes the rate of evaporation below the bubbles.
In these experiments, the cavities had been made in the centers of a series of pillars on the fabric’s surface. These pillars, blended with nanostructures, promote wicking of liquid from the rotten to their tops, and this enhances the boiling job by offering extra surface enlighten uncovered to the water. In combination, the three “tiers” of the skin texture — the cavity separation, the posts, and the nanoscale texturing — present a tremendously enhanced efficiency for the boiling job, Music says.
“These micro cavities give an explanation for the enlighten the build bubbles near up,” he says. “But by setting apart these cavities by 2 millimeters, we separate the bubbles and lower the coalescence of bubbles.” At the identical time, the nanostructures promote evaporation below the bubbles, and the capillary action induced by the pillars supplies liquid to the bubble rotten. That maintains a layer of liquid water between the boiling surface and the bubbles of vapor, which boosts the most warmth flux.
Photo shows how bubbles rising from a heated surface are “pinned” in teach locations attributable to particular surface texturing, in must spreading out over the entire surface. Credit: Courtesy of the researchers
Although their work has confirmed that the combination of these kind of surface therapies can work and discontinuance the desired outcomes, this work changed into as soon as achieved below little-scale laboratory prerequisites that would perchance well per chance furthermore no longer with out explain be scaled as a lot as purposeful devices, Wang says. “All these constructions we’re making are no longer supposed to be scaled in its present fabricate,” she says, however somewhat had been aged to instruct that the kind of gadget can work. One next step will be to procure replace programs of making these kind of surface textures so these programs would perchance well per chance furthermore extra with out explain be scaled as a lot as purposeful dimensions.
“Showing that we are capable of defend watch over the skin on this kind to get enhancement is a first step,” she says. “Then the next circulation is to specialize in extra scalable approaches.” To illustrate, even supposing the pillars on the skin in these experiments had been created using natty-room programs generally aged to fabricate semiconductor chips, there are different, less annoying programs of making such constructions, equivalent to electrodeposition. There are also a range of different programs to fabricate the skin nanostructure textures, a pair of of that would perchance well per chance furthermore very effectively be extra with out explain scalable.
There’ll be some critical little-scale applications that would perchance well per chance furthermore exhaust this job in its present fabricate, equivalent to the thermal management of digital devices, an enlighten that is turning into extra critical as semiconductor devices get smaller and managing their warmth output becomes ever extra critical. “There’s positively a enlighten there the build here’s if truth be told critical,” Wang says.
Even these forms of applications will interact some time to fabricate because generally thermal management systems for electronics exhaust liquids different than water, identified as dielectric liquids. These liquids gain different surface tension and different properties than water, so the size of the skin aspects would must be adjusted accordingly. Work on these differences is certainly one of the most next steps for the continuing analysis, Wang says.
This similar multiscale structuring methodology would perchance well per chance furthermore be applied to different liquids, Music says, by adjusting the size to account for different properties of the liquids. “These forms of critical parts would perchance well per chance be changed, and that would perchance well per chance be our next step,” he says.
Reference: “Three-Tier Hierarchical Constructions for Incorrect Pool Boiling Heat Switch Performance” by Youngsup Music, Carlos D. Díaz-Marín, Lenan Zhang, Hyeongyun Cha, Yajing Zhao and Evelyn N. Wang, 20 June 2022, Developed Provides.
DOI: 10.1002/adma.202200899
The personnel also included Carlos Diaz-Martin, Lenan Zhang, Hyeongyun Cha, and Yajing Zhao, all at MIT. The work changed into as soon as supported by the Developed Analysis Projects Company-Energy (ARPA-E), the Air Force Office of Scientific Analysis, and the Singapore-MIT Alliance for Analysis and Abilities, and made exhaust of the MIT.nano facilities.