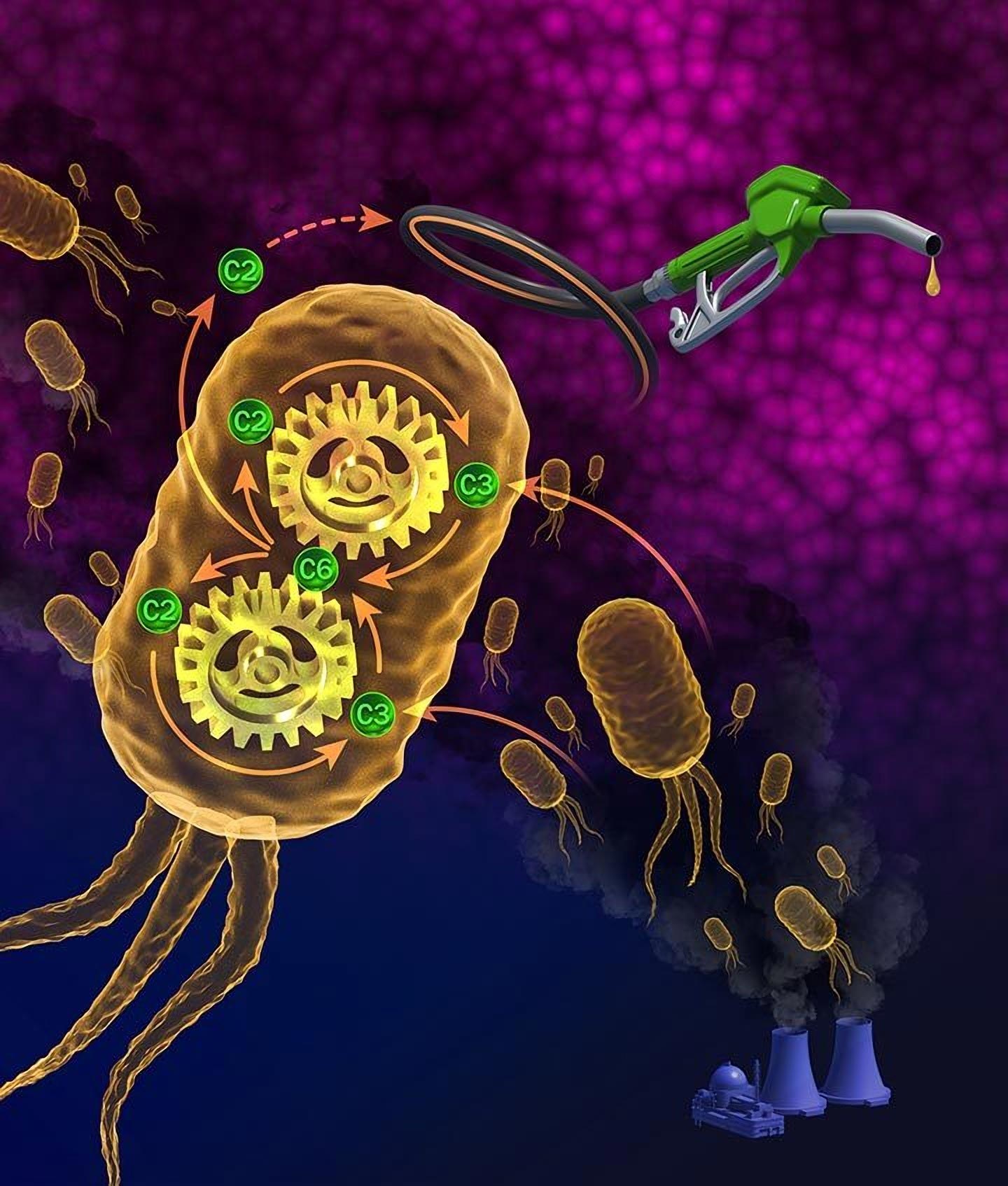
Bicyclic Carbon Fixation—NREL scientists occupy designed a pathway for speeding up CO2 fermentation in some species of micro organism. The ensuing molecule—acetyl-CoA, with its two unfamiliar carbon handles (C2)—could also be previous to create a unfold of well-known commodity fuels and chemical compounds. Credit score: Resolve by Besiki Kazaishvili, NREL
Scientists Mapped Out a “Bicyclic Carbon Fixation” Pathway for Rushing Up Gasoline Fermentation in Essentially educated Micro organism
Bakers ferment the dough for a well-risen loaf of bread. Likewise, brewers ferment wheat and barley for a delicate, malty glass of beer. And as nature’s major bakers and brewers, some microbes can attain even more. In actuality, particular species of micro organism ferment carbon dioxide (CO2) fuel to create their have vitamins of exchange. This would be leveraged to back energize our world.
This out of the ordinary ability—fermenting CO2 into chemical energy—isn’t lost on scientists who leer the nuanced and refined chemical reactions in micro organism.
Among them is Nationwide Renewable Vitality Laboratory (NREL) researcher Wei Xiong, who stated that fuel-fermenting micro organism offer classes on turning raze gases luxuriate in CO2 into sustainable fuels.
“CO2 removal and conversion are of world passion as CO2 is the excellent heat-trapping (greenhouse) fuel in the atmosphere. Pathways for CO2 fixation are a crux,” Xiong explained. “We now occupy a unfamiliar passion in designing unusual CO2 fixation avenues in micro organism to back them synthesize key biofuel precursors, as an illustration, acetyl-CoA.”
Acetyl-CoA is basically the most well-known ingredient for making multiple fuel chemical compounds, alongside with fatty acids, isopropanol, and butanol. And as detailed in a paper that became currently printed in the journal Nature Synthesis, Xiong and his colleagues occupy shown toughen the production of the fuel precursor the usage of a unusual pathway in fuel-fermenting micro organism.
By doing so, they brighten the possibility of the usage of natural tips on how to take hold of and convert CO2 on the industrial scale.
Easy Carbon Accounting: C1 + C1 = C2Naturally, fuel-fermentation in micro organism follows a linear sequence of reactions, identified to scientists as the Wooden-Ljungdahl pathway. This became named after Professors Harland G. Wooden and Lars G. Ljungdahl who stumbled on it in the 1980s. In easy phrases, enzymes strip CO2 of its carbon the usage of the electrical energy from nearby hydrogen or carbon monoxide fuel. They then affix two of these one-carbon atoms (C1) onto an even bigger molecule already unusual in the micro organism, called coenzyme A (CoA). By attaching two carbon handles (C2) to this helper molecule, they turn out to be more without complications accessible for diversified reactions.
The closing consequence? Acetyl-CoA, a more energy- and carbon-dense molecule that supports the micro organism’s inform. Furthermore it’s miles a to hand precursor for making treasured, native weather-pleasant biofuels.
Alternatively, despite its cleverness, the Wooden-Ljungdahl pathway by myself won’t be adequate for industrial snarl. Plus, its seemingly easy math (C1 + C1 = C2) is principally the final consequence of a dizzying choice of chemical reactions.
“Engineering this pathway to toughen efficiency is entertaining attributable to the enzymes’ complexity,” Xiong explained.
To sidestep bettering the Wooden-Ljungdahl pathway straight away, the researchers space out to conceptualize an absolutely unusual pathway for making acetyl-CoA. Utilizing an NREL-developed pc model called PathParser—and reveal-of-the-art genetic tools—the personnel invented a unusual CO2-fixing pathway in a species of fuel-fermenting micro organism called Clostridium ljungdahlii.
In the cease, the arithmetic works out the same: C1 + C1 = C2.
But to receive there, it comprises a pair of parallel reactions—a carbon-fixing bicycle with two wheels working together to take hold of CO2, remodel it the usage of a series of chemical gears, and redirect it to propel acetyl-CoA know-how forward (illustrated in the resolve on the raze of the online page). If added to fuel-fermenting micro organism, the pathway would possibly possibly complement the Wooden-Ljungdahl pathway to more efficiently yield acetyl-CoA.
Can We Ferment Our Manner to Carbon-Neutrality?There is never this form of thing as a shortage of raze gases on the unusual time, and right here is susceptible to live exact well into the future. Millions of hundreds CO2 are released yearly by heavy industry—a byproduct of refining biofuels, making steel, or mixing concrete. Scientists are exploring technologies for capturing and storing—better aloof the usage of—CO2 well earlier than it ever reaches the atmosphere.
“In the context of world warming and native weather swap, scientists uncover unusual alternate choices from microbial metabolism for changing CO2 to fuels and chemical compounds,” Xiong stated. “Gasoline-fermenting micro organism the truth is repair CO2 and describe a carbon-negative components for assembly our energy and environmental calls for.”
Who better to be taught from than fuel-fermenting micro organism that occupy mounted CO2 with ease for hundreds and hundreds of years?
Reference: “Acetyl-CoA synthesis by a bicyclic carbon-fixing pathway in fuel-fermenting micro organism” by Chao Wu, Jonathan Lo, Chris Urban, Xiang Gao, Bin Yang, Jonathan Humphreys, Shrameeta Shinde, Xin Wang, Katherine J. Chou, PinChing Maness, Nicolas Tsesmetzis, David Parker and Wei Xiong, 23 June 2022, Nature Synthesis.
DOI: 10.1038/s44160-022-00095-4
This study became supported in section by a U.S. Department of Vitality Bioenergy Applied sciences House of job Co-Optimization of Fuels and Engines mission and NREL’s Laboratory Directed Research and Pattern program.