By Victoria Gill
Science correspondent, BBC News
Image provide, College of Bristol
Image caption, Exceptional X-ray scanning ways revealed the 1mm creature in gorgeous detail
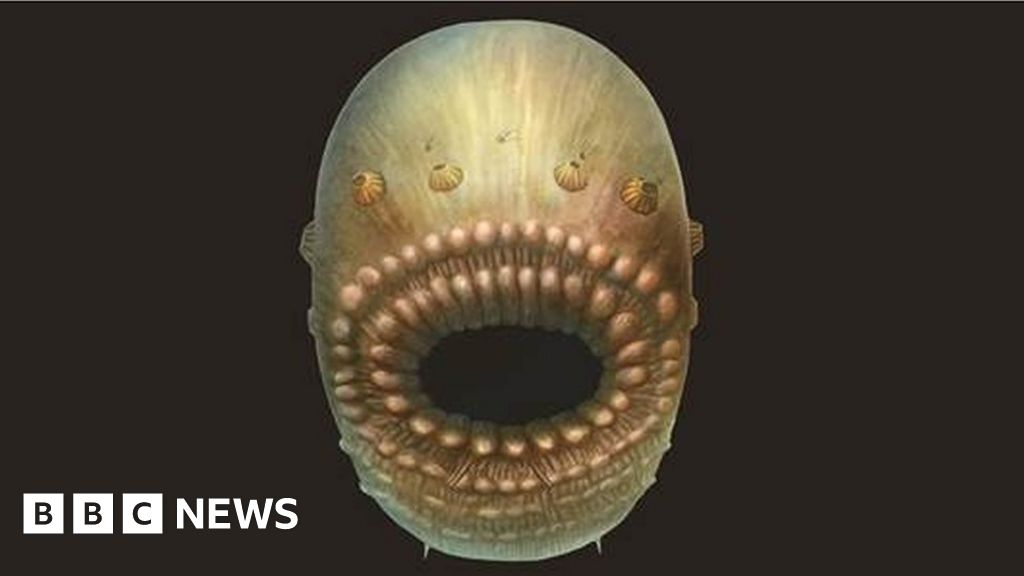
Scientists hiss they’ve solved an evolutionary thriller spirited a 500 million-12 months-venerable puny, spiny creature with a mouth but no anus.
When it turned into as soon as chanced on in 2017, it turned into as soon as reported that the diminutive fossil of this sack-esteem marine beast would be folk’ earliest-identified ancestor.
The aged animal, Saccorhytus coronarius, turned into as soon as tentatively placed into a personnel known as the deuterostomes.
These are the worn ancestors of vertebrates – including folk.
A brand new explore now suggests Saccorhytus must be attach into an totally assorted personnel of animals.
A personnel of researchers in China and the UK conducted a in fact detailed X-ray evaluation of the creature, and concluded that it belongs to a personnel known as the ecdysozoans – ancestors of spiders and insects.
One provide of this evolutionary confusion turned into as soon as the animal’s lack of an anus.
Emily Carlisle, a researcher who studied Saccorhytus intimately, explained to BBC Radio 4’s Inner Science: “It be quite advanced – [most] ecdysozoans possess an anus, so why did now not this one?”
One “racy option”, she acknowledged, is that an even earlier ancestor of this complete personnel did now not possess an anus, and that Saccorhytus evolved after that.
“It would be that it misplaced it in the course of its possess evolution – perchance it did now not need one because it’ll true take a seat in a single location with one opening for every thing.”
The fundamental motive though, for the “repositioning” of Saccorhytus on the Cambrian tree of lifestyles is that, on the preliminary examination, holes that surrounded its mouth were interpreted as pores for gills – a worn feature of deuterostomes.
When scientists looked in more detail – utilizing highly efficient X-rays to perceive the 1mm creature carefully – they realised that these were in fact the depraved of spines that had snapped off.
Scientists discovering out these fossils strive to arena each animals on a tree of lifestyles – considerable esteem a family tree – enabling them to fabricate an image to realize where they came from and the blueprint in which they evolved.
“Saccorhytus would possess lived in the oceans – in the sediment with its spines maintaining it in arena,” explained Ms Carlisle, who’s based totally totally at the College of Bristol.
“It would perchance per chance perchance, we maintain, possess true sat there – in a in fact habitual atmosphere with hundreds animals that can possess looked esteem some creatures alive at present time, but plenty that looked totally alien.”
Image provide, Cambridge College
Image caption, Artist’s reconstruction of Saccorhytus coronarius, in accordance to the usual fossil finds. The explicit creature turned into as soon as doubtlessly no higher than a millimetre in size
The rocks containing these Cambrian fossils are easy being studied.
“There is so considerable we can easy study about its atmosphere,” Ms Carlisle added.
“The more I explore palaeontology, the more I realise how considerable is missing. Via this creature and the sector it lived in, we’re in fact true scratching the surface.”
Image provide, College of Bristol
Image caption, Saccorhytus turned into as soon as a spiky sack-esteem creature with a mouth, but no anus
Listen to more tales from Inner Science on BBC Sounds
Follow Victoria on Twitter