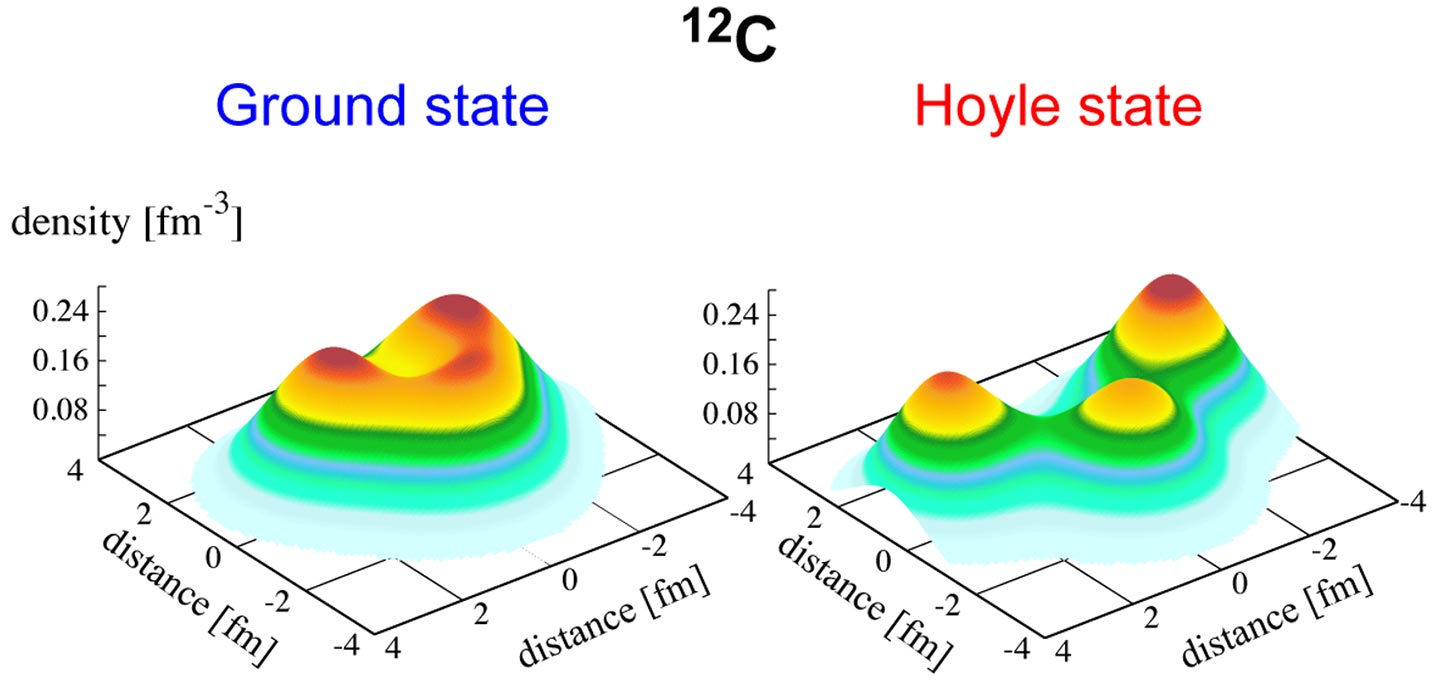
These laptop simulations account for the structures of carbon-12 in the unstable, enraged Hoyle narrate and as a stable ground narrate, the stuff of life. Credit rating: Mumble courtesy of James Vary/Iowa Convey College
With the support of the realm’s most great supercomputer and new synthetic intelligence tactics, an worldwide personnel of scientists has theorized how the phenomenal stipulations in stars fabricate carbon-12, which they dispute as “a excessive gateway to the starting up of life.”
The researchers’ significant ask develop into: “How does the cosmos fabricate carbon-12?” said James Vary, a professor of physics and astronomy at Iowa Convey College and a longtime member of the learn collaboration.
“It appears it’s hard to fabricate carbon-12,” Vary said.
It takes the phenomenal warmth and pressures interior stars or in stellar collisions and explosions to create emergent, unstable, enraged-narrate carbon nuclei with three loosely linked clumps, every with two protons and two neutrons. A fraction of these unstable carbon nuclei can shoot off a exiguous bit extra energy in the form of gamma rays and turn out to be the stuff of life, stable carbon-12.
A learn paper lately printed on-line by the journal Nature Communications describes the researchers’ supercomputer simulations and ensuing scheme for the nuclear structure of carbon that favors its formation in the cosmos. The corresponding creator is Takaharu Otsuka of the College of Tokyo, the RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based mostly fully mostly Science, and the Evolved Science Be taught Center of the Japan Atomic Vitality Company.
The paper describes how alpha particles – helium-4 atoms, with two protons and two neutrons – can cluster to form worthy heavier atoms, including an unstable, enraged carbon-12 narrate continuously called the Hoyle narrate (predicted by theoretical astrophysicist Fred Hoyle in 1953 as a precursor to life as we ticket it).
The researchers write that this alpha-particle clustering “is a actually arresting and charming scheme and is indeed plausible because the (alpha) particle is particularly stable with a perfect binding energy.”
To take a look at the hypothesis, the researchers ran supercomputer simulations, including calculations on the Fugaku supercomputer at the RIKEN Center for Computational Science in Kobe, Japan. Fugaku is listed because the most great supercomputer in the realm and is thrice extra great than No. 2, in accordance with the most trendy TOP500 supercomputer rankings.
Vary said the researchers also did their work ab initio, or from first guidelines, that method their calculations were in accordance to known science and didn’t include extra assumptions or parameters.
They also developed tactics in statistical studying, a division of computational synthetic intelligence, to convey alpha clustering the Hoyle narrate and the eventual manufacturing of stable carbon-12.
Vary said the personnel has worked for bigger than a decade to develop its instrument, refine its supercomputer codes, walk its calculations and work out smaller considerations whereas elevate to the sizzling work.
“There’s rather plenty of subtlety – rather plenty of arresting interactions happening in there,” Vary said.
The general calculations, bodily portions and theoretical subtlety match what experimental data there’s on this nook of nuclear physics, the researchers wrote.
So that they deem they’ve some general answers in regards to the origins of carbon-12. Vary said that ought to manual to extra reviews shopping for “fine-grain element” in regards to the route of and the tactic in which it works.
Used to be carbon manufacturing, for instance, mostly the implications of interior processes in stars? Vary asked. Or develop into it supernova superstar explosions? Or collisions of vital-dense neutron stars?
One thing is now particular to the researchers: “This nucleosynthesis in low environments produces rather plenty of stuff,” Vary said, “including carbon.”
Reference: “α-Clustering in atomic nuclei from first guidelines with statistical studying and the Hoyle narrate persona” by T. Otsuka, T. Abe, T. Yoshida, Y. Tsunoda, N. Shimizu, N. Itagaki, Y. Utsuno, J. Vary, P. Maris and H. Ueno, 27 April 2022, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29582-0
As well to James Vary and Pieter Maris of Iowa Convey College and Takaharu Otsuka of the College of Tokyo, the learn personnel entails:
Takashi Abe of the RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based mostly fully mostly Science and the Center for Nuclear Stumble on at the College of TokyoTooru Yoshida of the Center for Nuclear Stumble on at the College of Tokyo and the Be taught Organization for Knowledge Science and TechnologyYusuke Tsunoda of the Center for Nuclear Stumble on at the College of TokyoNoritaka Shimizu of the Center for Nuclear Stumble on at the College of TokyoNaoyuki Itagaki of the Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics at Kyoto UniversityYutaka Utsuno of the Evolved Science Be taught Center of the Japan Atomic Vitality Company and the Center for Nuclear Stumble on at the College of TokyoAnd Hideki Ueno of the RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based mostly fully mostly Science
Read More