Human eggs are designed to preserve out for a lengthy haul. When an particular particular person is born with a female reproductive plan, they’ve already developed the total eggs they’ll have for the comfort of their lifestyles. Yet, the ovaries’ roughly 1 to 2 million immature egg cells, is called oocytes, can preserve wholesome and be efficiently fertilized for up to 50 years, hinting to reproductive scientists that they must have a secret technique to steer obvious of wound for goodbye. Now, a crew of developmental biologists primarily based mostly in Barcelona, Spain, have chanced on that a key piece of oocytes can shift into a “standby battery mode,” maintaining the finite reserve for longer.
A gaze published on July 20 in the journal Nature finds that the mitochondria in oocytes tap into a obvious energy pathway that sidesteps the manufacturing of free radicals—chemical molecules that can wreak havoc on DNA, proteins, and cell partitions. The findings carry new gentle to the longevity of these cells and would possibly well per chance doubtlessly aid approach fertility concepts.
“Female fertility decreases by age, and whereas you happen to have a look at demographic reviews, increasingly more girls procure to provide birth of their mid-30s,” says Elvan Böke, senior author of the gaze and neighborhood chief in the Cell and Developmental Biology Program at the Heart for Genomic Rules in Barcelona. But spherical this age, “oocyte quality decreases, and that accounts for the bulk of female fertility complications,” she notes.
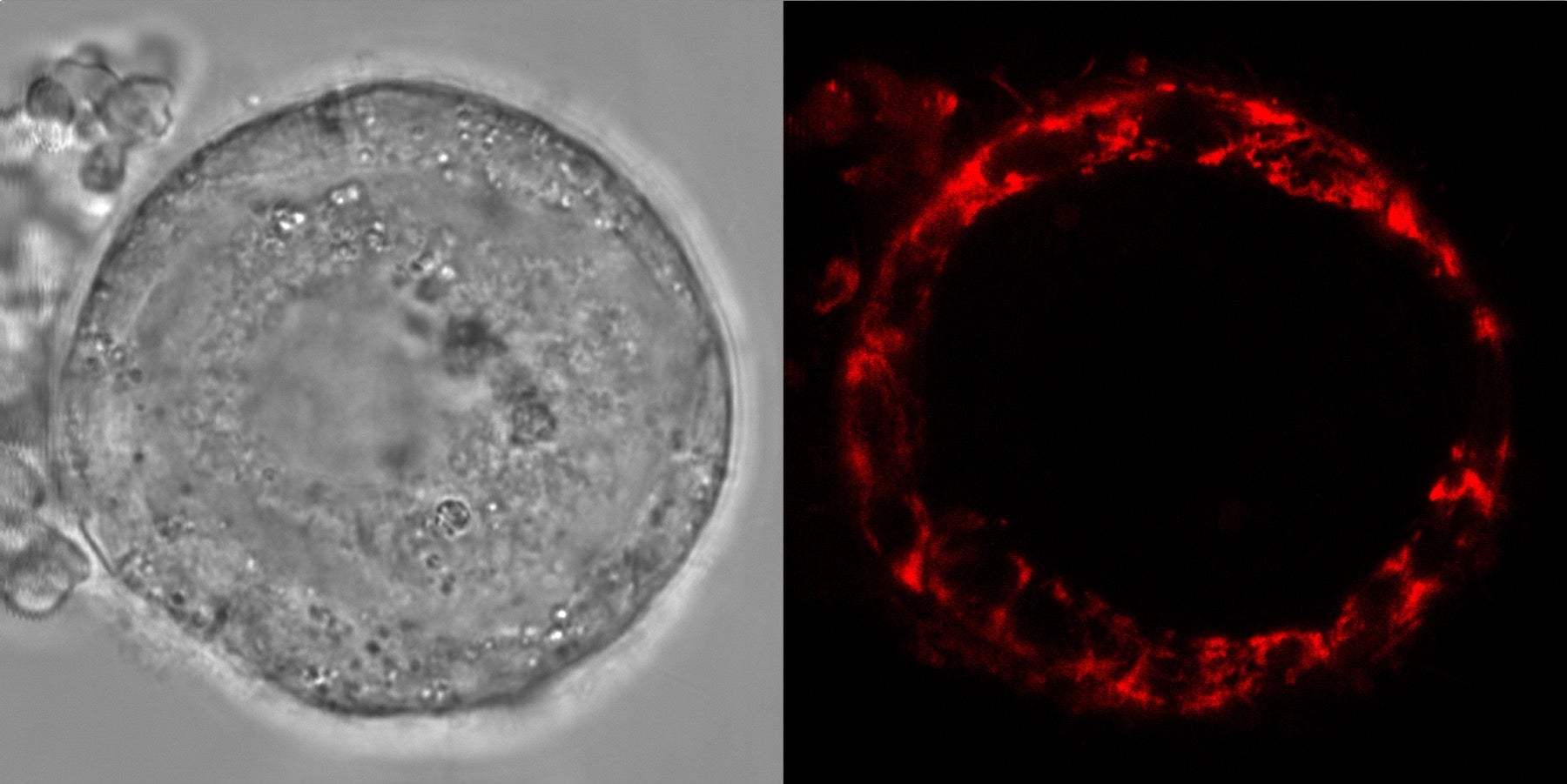
Human oocytes are in particular irregular, says Böke. Given our prolonged lifespans, the cells must remain dormant in the body for a few years—but now not like other lengthy-lived cells admire neurons, they’ll’t regenerate, and any wound would possibly well per chance affect the effectively being of the slight one. It’s a poor, but quite successful technique that’s now not effectively understood, explains Böke. “Oocytes are studied slight or no in the literature because of the accessing them is awfully, very laborious,” she says. Old research on other species imply that unprecedented oocytes have a sluggish metabolism, which enables for lengthy-term steadiness. What meaning for the cells’ lengthy-term survival, nevertheless, is level-headed a mystery.
“These cells reside very lengthy, and presumably, they have something else occurring in contrast with other cells,” Bökesays. “We wanted to know what the oocyte concepts are to aid youthful cytoplasm and cell structure for a few years.”
Böke teamed up with lead gaze author and genomic researcher Aida Rodríguez-Nuevo and other colleagues to compare the process of mitochondria in oocytes, particularly hunting for traces of wicked reactive oxygen species (ROS), or free radicals. In obvious forms of properly functioning cells, these molecules can aid usher along most significant processes. But when their ranges are too high, they’ll reason loads of wound, and even reason most cancers in some conditions. “You don’t genuinely are looking out to have loads of them,” says Böke.
[Related: Why doctors still don’t understand the side effects of hormonal birth control]
Mitochondrial factors are one of many principle causes reactive oxygen builds up in the body. Because the powerhouses of cells, mitoc